4. Rosacea: The Red-Faced Skin Disorder
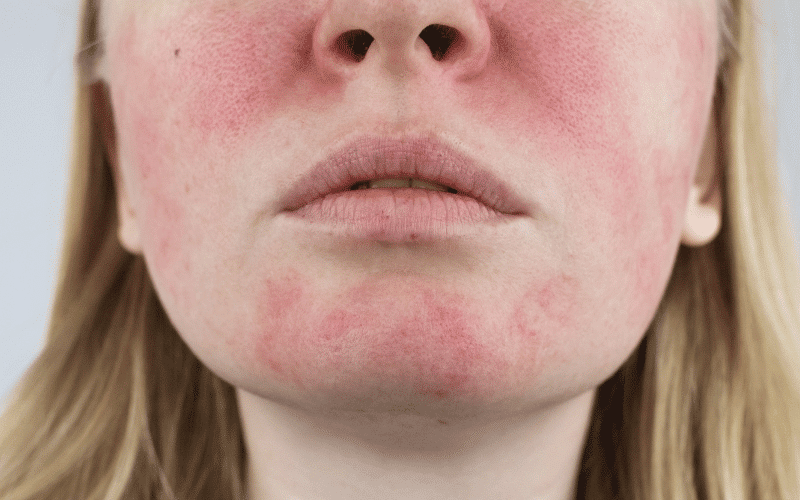
Facial Redness and Flushing: Early Signs of Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels. It usually begins with a tendency to blush or flush more easily than others and can progress to persistent redness in the central part of the face. Rosacea typically affects adults over the age of 30 and is more common in people with fair skin.
Bumps, Pimples, and Swelling: Advanced Rosacea Symptoms
As rosacea progresses, other symptoms may develop, including small, red bumps or pus-filled pimples, and thickening of the skin. In some cases, rosacea can also cause eye problems, such as dryness, irritation, and swollen, red eyelids. This is known as ocular rosacea.
Triggers and Aggravating Factors: What Can Worsen Rosacea?
Various factors can trigger or worsen rosacea symptoms, including exposure to sunlight, hot or cold temperatures, wind, spicy foods, alcohol, stress, and certain skincare products. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage and reduce rosacea symptoms.
Treatment and Management: Reducing Redness and Controlling Symptoms
There is no cure for rosacea, but symptoms can be managed through a combination of treatments and lifestyle changes. Topical treatments, such as metronidazole or azelaic acid, can help reduce redness and inflammation.
Oral antibiotics or isotretinoin may be prescribed for more severe cases. Laser or light therapy can also be used to reduce redness and visible blood vessels. In addition to medical treatments, avoiding triggers and adopting a gentle skincare routine can help keep rosacea symptoms under control. (4)