5. Hives: The Itchy, Raised Skin Welts
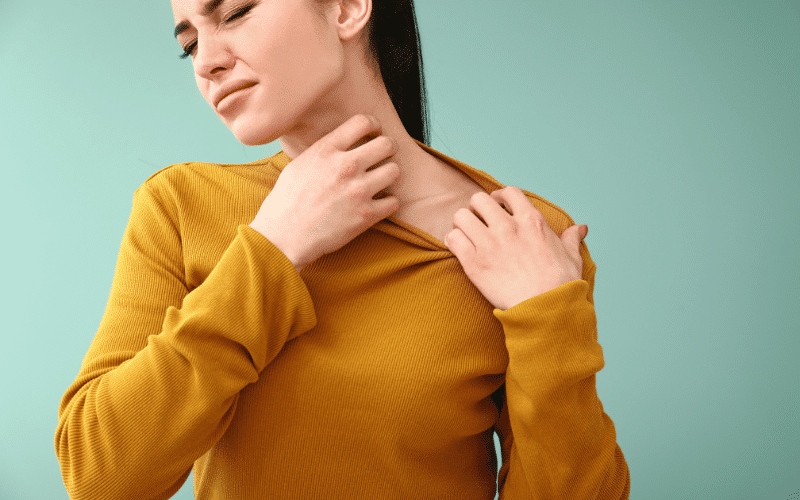
Raised, Red Bumps: The Distinct Appearance of Hives
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, red, itchy bumps on the skin that can appear suddenly and typically last for a few hours to a day. Hives can vary in size and shape and may join together to form larger areas, called plaques. They can appear anywhere on the body and are usually a sign of an allergic reaction.
Allergens and Triggers: What Causes Hives?
Hives can be triggered by a variety of allergens, including foods (such as peanuts, shellfish, or eggs), medications (like antibiotics or pain relievers), insect bites or stings, and contact with certain plants or substances. In some cases, hives can also be triggered by physical factors, such as heat, cold, pressure, or exercise.
Acute vs. Chronic Hives: Duration Matters
Hives can be classified as acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting more than six weeks). Acute hives are more common and are usually caused by an allergic reaction, while chronic hives are often more challenging to pinpoint and may be related to an underlying health condition or autoimmune disorder.
Treatment and Prevention: Relieving Itchiness and Avoiding Triggers
Treatment for hives typically involves antihistamines to reduce itching and swelling. In more severe cases, corticosteroids or other medications may be prescribed to suppress the immune system’s response.
Identifying and avoiding the triggers that cause hives can help prevent future occurrences. If the cause of hives is unknown, working with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and develop a management plan is essential. (5)