10. Scabies – A Highly Contagious Skin Infestation
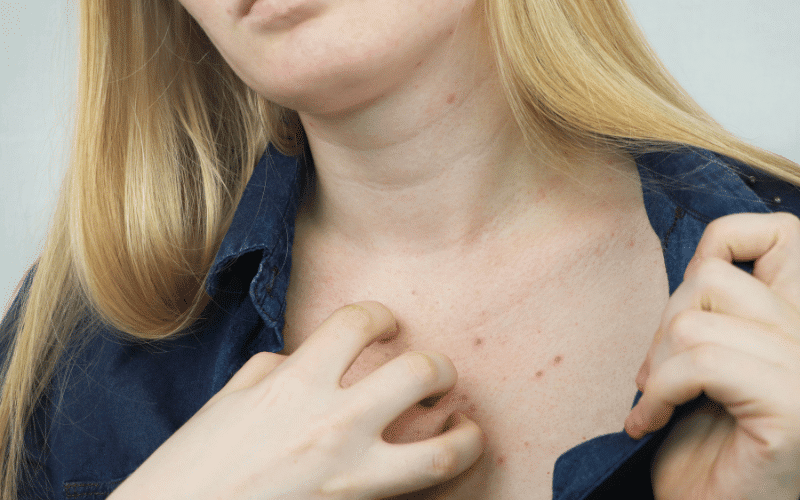
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which burrows into the skin’s upper layer and lays eggs. The infestation results in an intensely itchy rash, characterized by small red bumps and blisters, typically appearing in skin folds, such as between the fingers, under the arms, or around the waist.
Scabies is spread through close physical contact or by sharing personal items, such as clothing, bedding, or towels, with an infested person. The mites can survive for up to 72 hours away from the human body, making it essential to treat both the person and their environment to prevent re-infestation.
Treatment for scabies involves the use of prescription creams or lotions containing a scabicide (a substance that kills the mites), which is applied to the entire body, usually left on for 8-14 hours, and then washed off. In some cases, oral medications may be necessary. It’s crucial to follow the treatment instructions carefully and to treat all household members and close contacts to prevent the spread of the infestation.
In addition to treating the person, it’s essential to launder all clothing, bedding, and towels in hot water and dry them on high heat. Items that cannot be washed should be sealed in a plastic bag for at least 72 hours to kill the mites. Vacuuming the home and disposing of the vacuum bag can also help remove mites from the environment.
If you suspect that you or a family member has scabies, consult your healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. (10)