7. Eczema – A Chronic Inflammatory Skin Condition
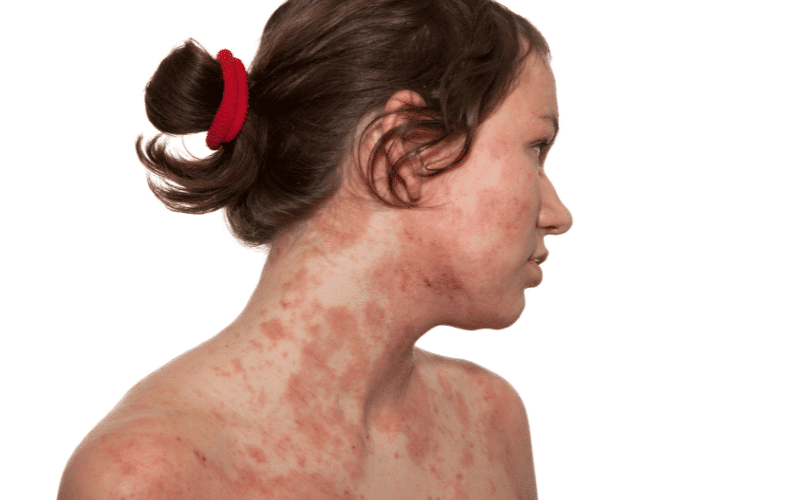
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and dry patches of skin. Eczema can affect people of all ages but is particularly common in children. The condition often appears on the face, neck, and the creases of the elbows and knees but can occur anywhere on the body.
The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it is thought to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Eczema is often associated with other allergic conditions, such as asthma and hay fever. Triggers for eczema flare-ups can include irritants (such as soaps, detergents, or certain fabrics), allergens (like pollen, pet dander, or certain foods), stress, and changes in temperature or humidity.
There is no cure for eczema, but the condition can be managed through proper skincare and the avoidance of known triggers. Treatment typically involves the use of emollients (moisturizers) to keep the skin hydrated, topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and antihistamines to alleviate itching. In more severe cases, prescription medications, such as topical calcineurin inhibitors or systemic immunosuppressants, may be necessary to control the condition.
If you suspect that you or your child has eczema, consult your healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. In addition, consider working with an allergist to identify potential triggers and develop strategies to minimize exposure. (7)