Introduction: Understanding and Managing Nosebleeds (Epistaxis)
Nosebleeds, or epistaxis, are a common condition that affects a wide range of individuals. Whether occurring spontaneously or as a result of specific triggers, they can be a source of discomfort and concern.
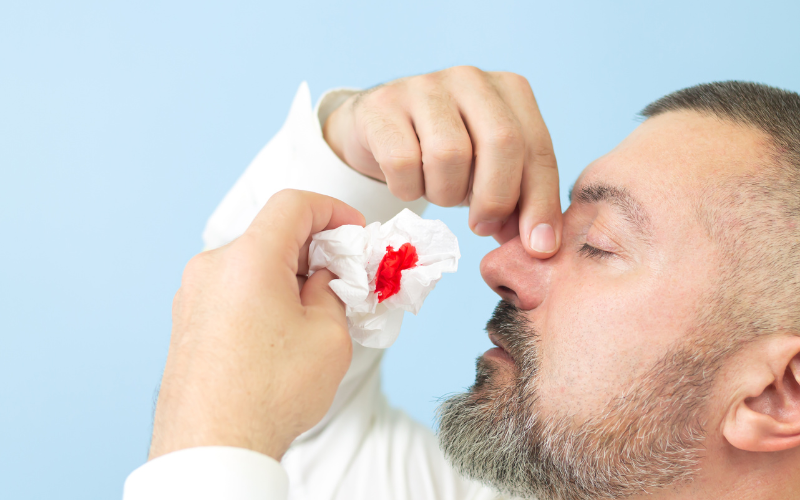
This article aims to provide in-depth insights and practical tips on managing nosebleeds. Understanding why nosebleeds occur is the first step in effective management. Various factors, ranging from dry air to medical conditions, can contribute to this phenomenon.
Nosebleeds are typically classified into two categories: anterior and posterior. Anterior nosebleeds, originating from the front part of the nose, are more common and usually easier to manage. Posterior nosebleeds, coming from deeper within the nose, can be more severe and often require medical attention.
Effective management of nosebleeds not only involves immediate actions to stop the bleeding but also encompasses preventive measures to reduce their frequency and severity. This article will guide you through ten strategies to effectively manage and prevent nosebleeds, tailored to various causes and severities. By adopting these practices, individuals can confidently handle nosebleeds, ensuring minimal disruption to their daily lives.
1. Pinch and Press – Your First Line of Defense Against Nosebleeds
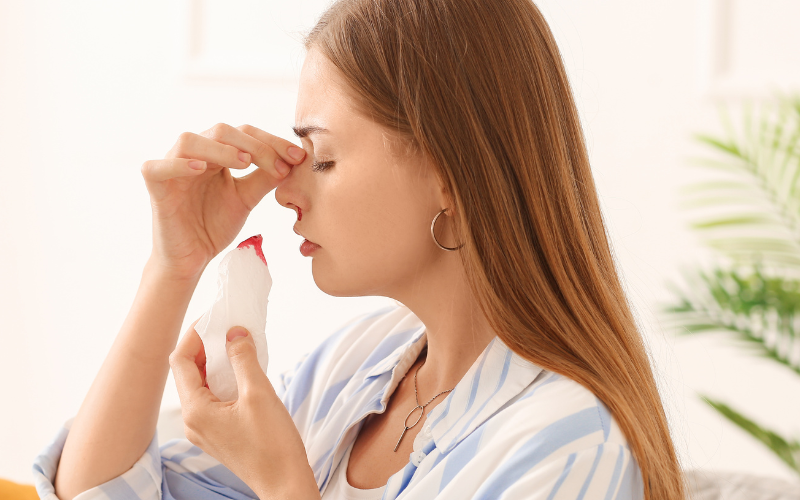

Pinching and pressing your nose is a widely endorsed first response to a nosebleed. This technique is straightforward yet effective.
It requires you to apply gentle pressure to the bleeding area. By doing so, you assist in compressing the blood vessels. This action plays a crucial role in controlling the bleed.
To properly execute this method, use your thumb and index finger. Gently pinch the soft part of your nose. Ensure that your grip is firm but not overly tight. Lean forward slightly. This posture is vital in preventing blood from flowing back into the throat.
Maintaining the pressure for about 10 to 15 minutes is crucial. During this time, it’s essential to stay calm. Breathe steadily through your mouth. Resist the urge to check if the bleeding has stopped too soon. Doing so can disrupt the clotting process.
After the bleeding stops, it’s important to avoid any actions that might trigger a recurrence. Refrain from blowing or picking your nose. Such actions can dislodge the delicate clots that have formed. (1)