Fact 12: Relationship with Other Diseases
Delve deeper into the narrative of gastric cancer, and intriguing links emerge with other diseases. The stomach, being central to our digestive system, interacts with various other organs and systems, leading to potential disease crossovers.
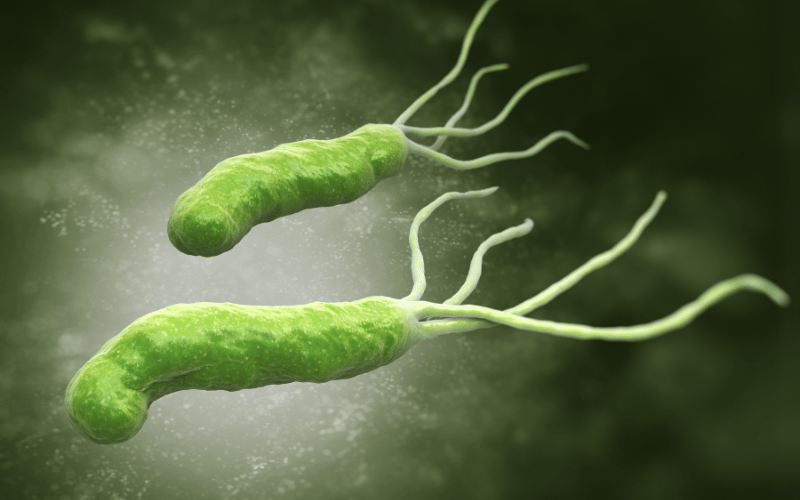
One of the most well-documented relationships is with Helicobacter pylori infections. This bacterium, when it colonizes the stomach lining, can lead to gastritis and ulcers. Over time, chronic infection can escalate to atrophic gastritis, a precursor to stomach cancer.
Additionally, there’s the link between gastric cancer and pernicious anemia, a condition where the stomach fails to produce a protein required for vitamin B12 absorption. This ailment, while seemingly distant from cancer, creates an environment within the stomach that’s conducive to malignancy.
Moreover, conditions like Menetrier’s disease, which thickens parts of the stomach lining, or common ailments like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which causes chronic acid reflux, have associations with higher stomach cancer risks. These links underscore the stomach’s vulnerability and its interconnectedness with other diseases. (12)