15. The Influence of High Triglyceride Levels
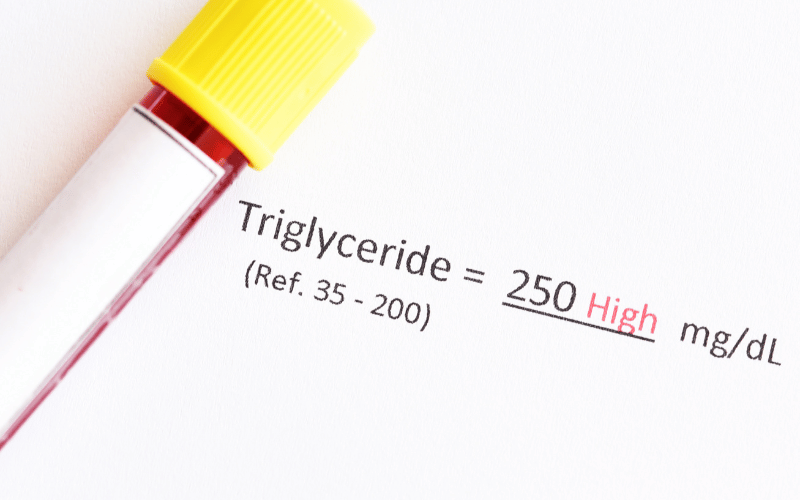
Elevated levels of triglycerides, a type of fat found in the blood, have been linked to an increased risk of acute pancreatitis. Severe hypertriglyceridemia, in particular, is a recognized cause of AP, requiring prompt recognition and intervention.
Healthcare providers should consider the possibility of hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis in patients with significantly elevated triglyceride levels, particularly when other common causes of AP are ruled out. Blood tests to measure lipid levels are essential in these cases to confirm the diagnosis and guide management.
Managing acute pancreatitis related to high triglyceride levels involves addressing the elevated lipid levels through dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and lipid-lowering medications. Supportive care to manage the symptoms of AP and prevent complications is also a critical component of the management plan.
In summary, elevated triglyceride levels are a significant risk factor for acute pancreatitis. Timely diagnosis, comprehensive management of lipid levels, and supportive care are key in preventing recurrent episodes of AP and ensuring optimal patient outcomes. (15)