Fact 10: Alcohol-Related Dementia and Brain Changes
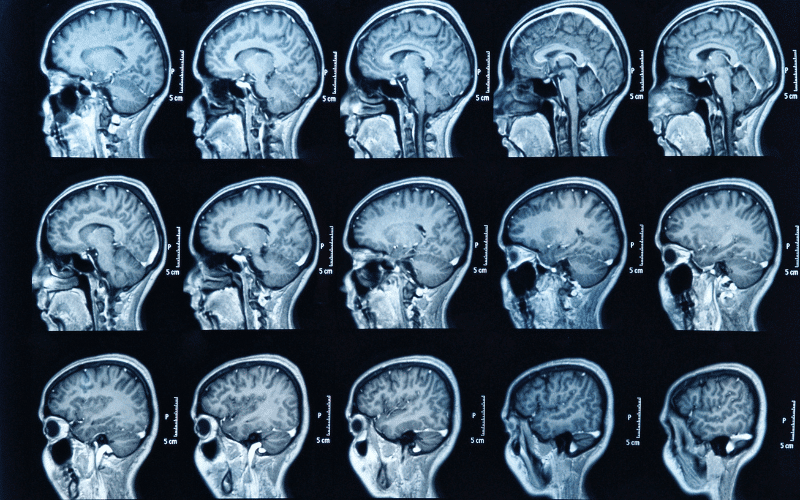
ARD is associated with significant changes in the brain. Chronic, heavy alcohol consumption can cause both structural and functional alterations in various brain regions, leading to the cognitive impairments seen in ARD.
Structurally, alcohol can cause a reduction in brain volume, known as brain atrophy. This is particularly evident in the frontal lobes, the area of the brain involved in executive functions like decision-making, planning, and impulse control. Brain scans of people with ARD often show enlarged ventricles (fluid-filled spaces in the brain), a characteristic sign of brain atrophy.
Functional changes can also occur. Alcohol disrupts the normal balance of neurotransmitters, the chemicals that facilitate communication between brain cells. This disruption can impair the functioning of various brain regions, contributing to the cognitive deficits associated with ARD.(10)