4. The Diagnostic Journey: Identifying Myoclonic Epilepsy
Diagnosing myoclonic epilepsy is a complex process that requires a careful and methodical approach. One of the first steps in this journey is often a detailed clinical evaluation, including a thorough review of the patient’s medical history and a comprehensive neurological examination.
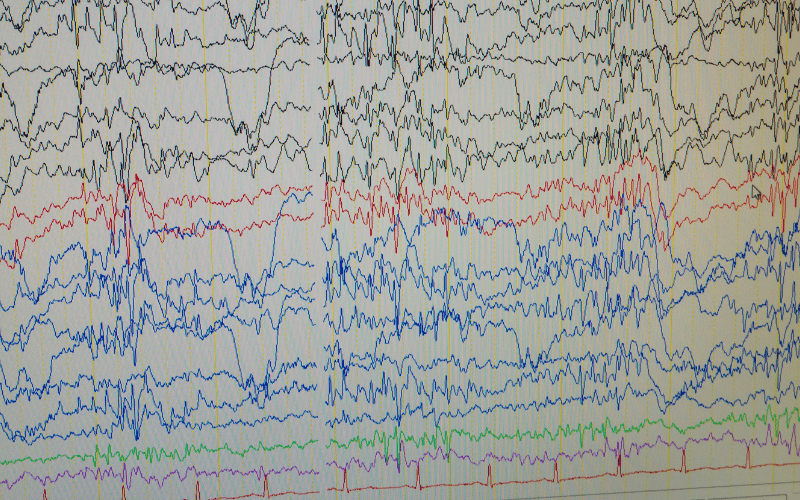
The cornerstone of diagnosing myoclonic epilepsy, however, is an electroencephalogram (EEG). This test records the brain’s electrical activity, providing valuable information on abnormal brain patterns characteristic of epilepsy. In myoclonic epilepsy, an EEG might reveal specific patterns like “polyspike and wave” discharges or “myoclonic discharges.”
Interestingly, sleep deprivation and hyperventilation are sometimes used during EEG as they can provoke myoclonic seizures, increasing the likelihood of capturing abnormal brain activity. This technique underscores the creativity and resourcefulness medical practitioners need to utilize when diagnosing complex conditions like myoclonic epilepsy.
Further, while EEG provides a crucial piece of the puzzle, it’s often necessary to combine it with other diagnostic tests for a definitive diagnosis. These might include Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to check for any structural brain abnormalities, or genetic testing if a hereditary form of myoclonic epilepsy is suspected. (4)