Introduction: Fearsome Word on Letter ‘C’
Differentiated thyroid cancer, a predominant type of thyroid malignancy, affects a considerable number of individuals globally each year. Due to its typically subtle symptomatology, it often eludes early detection, which is a crucial factor in successful treatment and prognosis. This article aims to illuminate the top ten symptoms associated with differentiated thyroid cancer, thereby promoting awareness and fostering timely medical intervention.
The thyroid gland, an essential part of our endocrine system, produces hormones that regulate numerous bodily functions. When cells in this butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of our neck start to grow and multiply abnormally, thyroid cancer can develop. There are several types of thyroid cancer, among which differentiated thyroid cancer, including papillary and follicular thyroid cancer, is the most common.
Differentiated thyroid cancer can occur in people of all age groups but is more prevalent in individuals in their 30s to 50s. While both men and women can be affected, the condition is more frequently seen in women. It is important to remember that a better understanding of the symptoms of this malignancy can be pivotal in its early detection and successful treatment.
Although the exact causes of differentiated thyroid cancer remain unknown, several risk factors contribute to its development. These include exposure to high levels of radiation, especially during childhood, a family history of thyroid disease or cancer, and certain inherited genetic syndromes. While the presence of one or more of these risk factors does not guarantee the development of thyroid cancer, they significantly increase the likelihood.
Now, let’s delve into the detailed discussion on the top ten symptoms of differentiated thyroid cancer. These symptoms can often be overlooked or attributed to less severe conditions. Awareness and recognition of these signs can help individuals seek timely medical attention, potentially saving lives.
Symptom 1. Swollen Lymph Nodes: The Signs Of Troubles
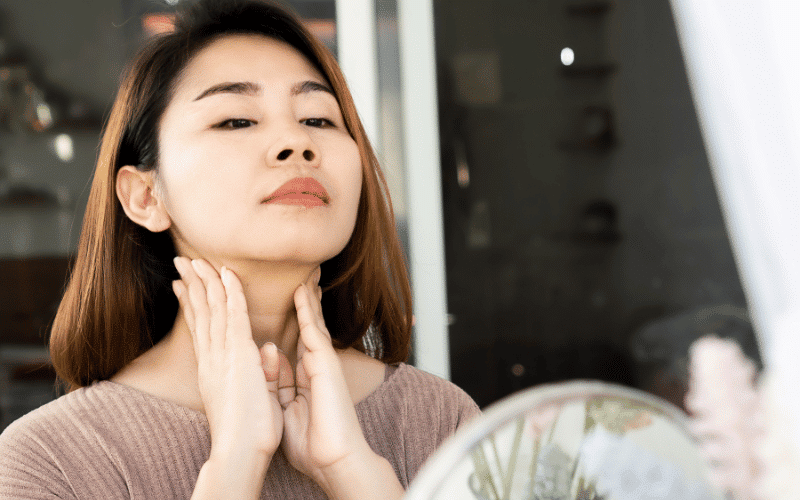

Our lymph nodes, tiny bean-shaped structures scattered throughout our body, play a crucial role in our immune response. In the case of differentiated thyroid cancer, these nodes, particularly those in the neck, can swell up and become palpable.
Cancer cells can spread, or metastasize, from the thyroid gland to the lymph nodes via lymphatic vessels. Once in the nodes, these cells can multiply and cause the nodes to enlarge, leading to noticeable swellings in the neck.
Swollen lymph nodes in thyroid cancer are typically firm, non-tender, and may move slightly upon touch. They might present as single or multiple lumps in the neck, often detected by patients while shaving or looking in the mirror. Some patients may even feel a sensation of fullness in the neck.
The detection of swollen lymph nodes is significant, as it can indicate advanced disease or aggressive tumor behavior. Therefore, it is crucial not to dismiss these swellings as mere ‘lumps’ and seek medical attention.
A swollen lymph nodes might be the body’s quiet distress call, hinting at differentiated thyroid cancer. While not every lump forecasts doom, it’s a symptom that requires serious attention. Unexplained swellings should never be dismissed or overlooked, for early detection holds the key to fighting differentiated thyroid cancer successfully. (1)