3. Thrombosis and Blood Clots – The Silent Threat of ET
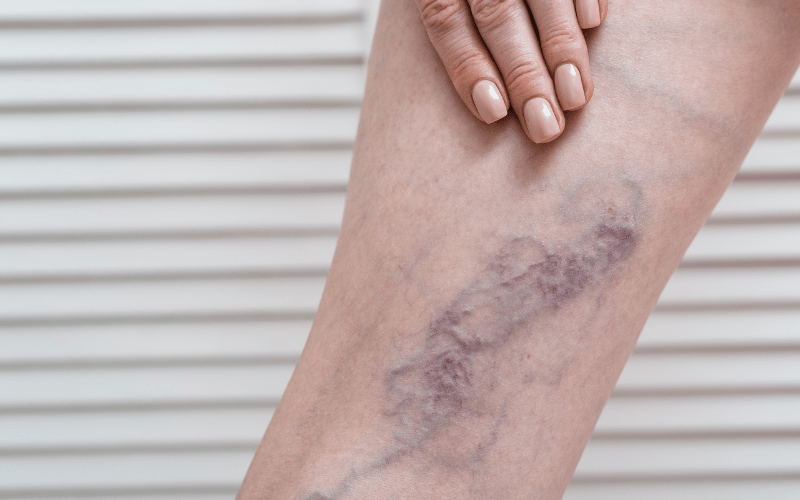
Thrombosis, or the formation of blood clots, is a serious concern in ET. These clots can occur in various parts of the body and present a significant health risk.
The heightened platelet count in ET patients contributes to this increased clotting tendency. Clots can lead to complications like stroke, heart attack, or deep vein thrombosis.
The symptoms of thrombosis can be subtle or even non-existent in some cases. This makes regular medical check-ups vital for ET patients. Physicians often monitor for signs of clotting as part of ongoing ET management. Patients should be aware of symptoms like swelling, redness, or pain in the limbs. These may indicate deep vein thrombosis, a common form of clotting.
In addition to physical symptoms, there are often no early warning signs of thrombosis. This necessitates a proactive approach to health monitoring. Patients are advised to maintain regular communication with their healthcare providers. They should also adopt lifestyle changes that reduce clotting risks, such as staying active and hydrated.
Effective management of thrombosis in ET involves a combination of medication and lifestyle adjustments. Anticoagulants or blood thinners are often prescribed to reduce clotting risks. These medications require careful monitoring and dosage adjustments. Patients must also be mindful of potential interactions with other medications. (3)