Introduction: Understanding Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is a common condition that affects many people, yet it often goes undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. In the following sections, we will present the 10 most common symptoms of ETD, along with an explanation of the condition, its underlying causes and treatment options. By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of ETD, which will enable you to identify the condition and seek professional help if needed.
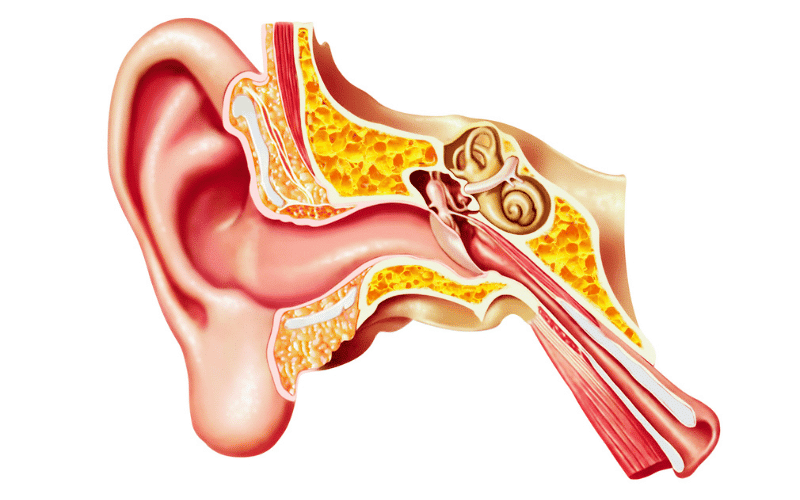
The eustachian tubes are small, narrow passages that connect the middle ear to the back of the throat. They play a critical role in maintaining the balance of air pressure between the middle ear and the outside environment. When these tubes become blocked or don’t function correctly, ETD occurs. This can lead to a range of uncomfortable symptoms and may impact an individual’s overall quality of life.
Eustachian tube dysfunction can be caused by various factors, including inflammation, infection, or blockage due to allergies or a cold. These factors can make it difficult for the eustachian tubes to open and close properly, leading to the pressure imbalance that causes ear pain. In some cases, structural abnormalities, such as a narrow or unusually shaped eustachian tube, can also contribute to ETD and its associated symptoms.
Now that you have a basic understanding of ETD, let’s delve into ten specific symptoms associated with this condition. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge to recognize and manage ETD effectively. Recognizing these symptoms is key to identifying and addressing ETD before it causes more serious complications.
Symptom 1. Persistent Ear Pain: A Common Indicator of ETD

Ear pain, medically known as otalgia, is often the first sign of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. This pain may be intermittent or constant, and its severity can range from a mild annoyance to a debilitating condition that affects your daily life.
The pain stems from pressure changes within the middle ear due to ETD. When the Eustachian tube doesn’t function properly, the pressure in the middle ear can’t be equalized, leading to discomfort or pain. This can be exacerbated by actions that naturally change your body’s internal pressure, such as yawning or swallowing.
To some, this ear pain may present as a feeling of “stuffiness” in the ear, as if the ear needs to “pop” but can’t. This feeling is similar to what one might experience during a rapid altitude change, like when an airplane ascends or descends.
Moreover, the pain might fluctuate in response to different activities. For instance, lying down might alleviate the pain for some, while it exacerbates it for others. Sleep disruptions due to this pain are common among ETD patients, underscoring the significant impact this condition can have on overall quality of life.
Instead of dismissing your persistent ear pain as just a side effect of a loud concert or a cold, view it as a sign that your body may be struggling with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. Finding the appropriate support could be the key to silencing the incessant throbbing and reclaiming your peace. (1)