Introduction: Journey through the Labyrinth of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
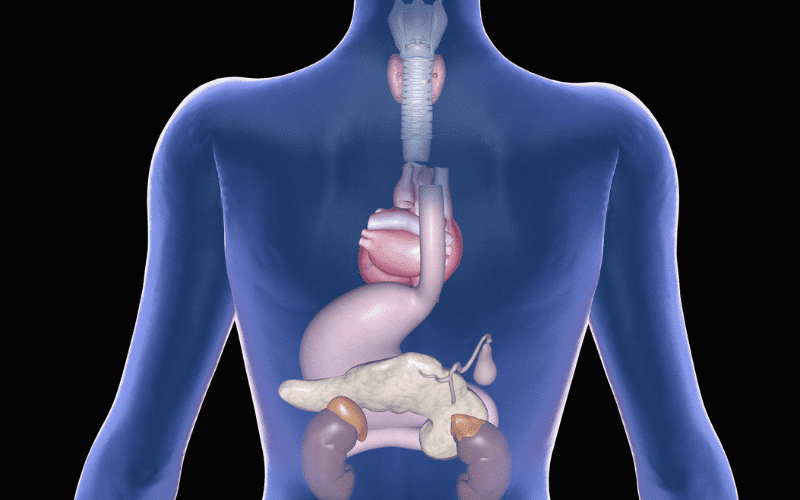
Within our bodies, there operates an intricate network of glands referred to as the endocrine system. These glands churn out hormones to regulate myriad body functions. However, when these workhorses of the human body begin to malfunction, the effects can be nothing short of havoc. Meet the Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN), a set of genetic disorders causing benign or malignant tumors to form in these hormone-producing glands.
Unraveling the web of MEN becomes essential for early detection, prompt intervention, and effective management. It’s an inherited disorder, so a meticulous study of family history often brings to light its lurking presence. The disorder exhibits itself in four types—MEN1, MEN2A, MEN2B, and FMEN1. Despite their shared origin, each type has distinct characteristics and impacts different glands.
MEN gives rise to tumors in several endocrine glands simultaneously, causing them to produce too much or too little of any hormone. As these hormones control numerous bodily functions, the effects of MEN are far-reaching. They can cause a plethora of symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe life-threatening conditions. However, the severity of symptoms often varies from person to person.
Unpacking the four types of MEN is critical to understanding their varying manifestations, paving the way for targeted treatments. This endeavor is more than an academic exercise—it is a necessary step in demystifying a complex condition that impacts lives deeply. It underscores the power of knowledge in the fight against genetic disorders and how it aids patients and their families in navigating the complexities of MEN.
We will dive deep into each type, drawing from the latest scientific research and clinical observations. We’ll explore the unique characteristics of each type, the glands they affect, the potential risks they pose, and the breakthroughs in managing them. The journey ahead is to enlighten ourselves about these conditions, unraveling the intricacies of MEN bit by bit.
Type 1: MEN1, The Unseen Interloper
The tale of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia begins with MEN1. This genetic condition bears the notorious distinction of wreaking havoc silently. Often, the symptoms stay camouflaged until hormonal imbalances become too glaring to ignore. This devious approach often delays the diagnosis of MEN1.
MEN1, or Wermer’s syndrome, primarily affects three glands—the parathyroid, pancreas, and pituitary. These glands, crucial cogs in the body’s hormone factory, produce essential hormones for various bodily functions. Under MEN1’s influence, they may develop benign tumors. These tumors often upend the hormone balance, leading to a multitude of health complications.
Dr. Paul Wermer, who first painted a clear picture of MEN1, lends his name to the syndrome. While MEN1 doesn’t always make it to the headlines, it accounts for a significant chunk of MEN cases. MEN1’s crafty nature makes it a formidable opponent, but vigilant medical professionals have their ways to corner it.
The diagnostic arsenal against MEN1 comprises a blend of genetic testing and hormone level monitoring. Genetic testing seeks out the presence of the MEN1 gene mutation. In parallel, monitoring hormone levels provides insights into whether the glands are overproducing hormones, another potential sign of MEN1. This combination approach helps pin down the elusive condition.
The study of MEN1 illuminates the complexity of the endocrine system and its susceptibility to genetic disruptions. While MEN1 might be a silent player, its effects are far from quiet. By diving deep into the nuances of this condition, we can appreciate the intricate dance of our hormones and the significance of their delicate balance. (1)