Symptom 6: Glandular Swelling: LCH’s Overt Display of Dominance
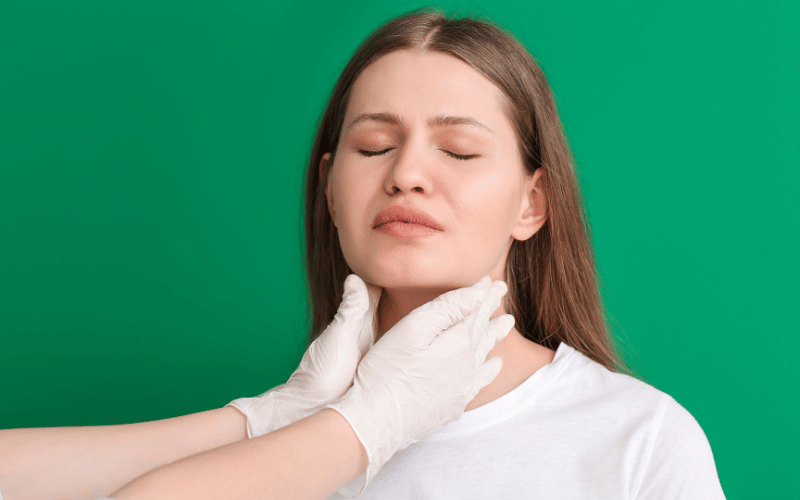
Swollen glands, particularly in the neck, armpit, and groin, stand as testament to the body’s fight against LCH. These swellings, known as lymphadenopathy, signify the immune system’s response to the infiltration of Langerhans cells.
At a glance, these swellings might seem similar to those arising from common infections. Yet, their persistence and the absence of other typical infection symptoms set them apart. Lymph nodes, acting as filters for harmful substances, become overrun with Langerhans cells in LCH.
As these nodes enlarge, they not only become palpable but can cause discomfort, especially if they press against neighboring structures. For instance, swollen glands in the neck might lead to difficulty in swallowing or a persistent sore throat.
While the glands themselves are the primary sites of swelling, their enlargement has ripple effects. They can impact neighboring organs, causing a cascade of symptoms that might seem unrelated at first glance.
LCH’s ability to cause glandular swelling is a stark reminder of its pervasive nature. It showcases how the disease, though microscopic in origin, can manifest in overt and palpable ways. (6)