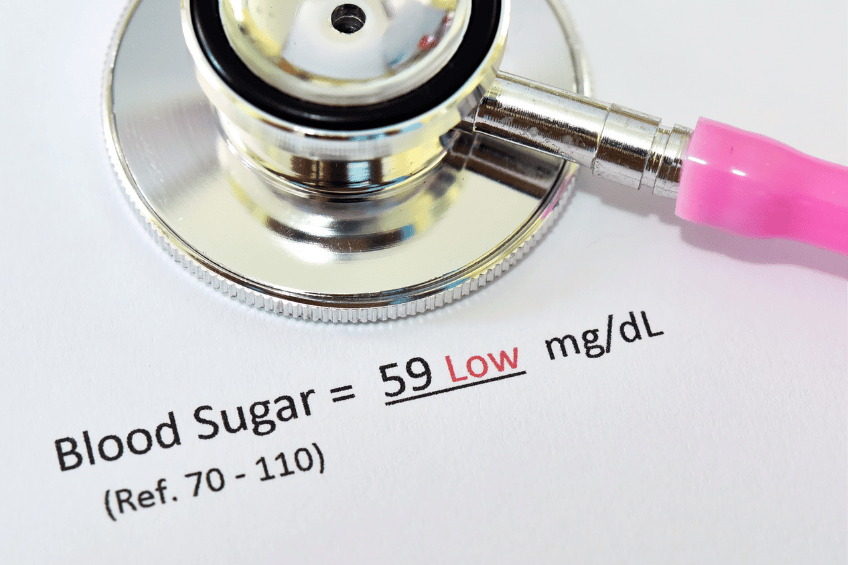Severe Low Blood Sugar.
Further lowering of blood sugar triggers the release of epinephrine (adrenaline), the “fight-or-flight” hormone. It is responsible for symptoms such as:
- Confusion, abnormal behavior (such as inability to complete routine tasks);
- Visual disturbances (such as blurred vision);
- Slurred speech or numbness;
- Drowsiness.
If blood sugar levels remain low, the brain does not get enough glucose and starves. Severe low blood sugar is below 54 mg/dL. If the level is this low, there is a chance of fainting and requiring assistance. [9] Severe low blood sugar has to be treated immediately, because it can lead to seizures, a coma, and even death. [1]