7. The Importance of Blood Sugar Monitoring in Diabetes Management
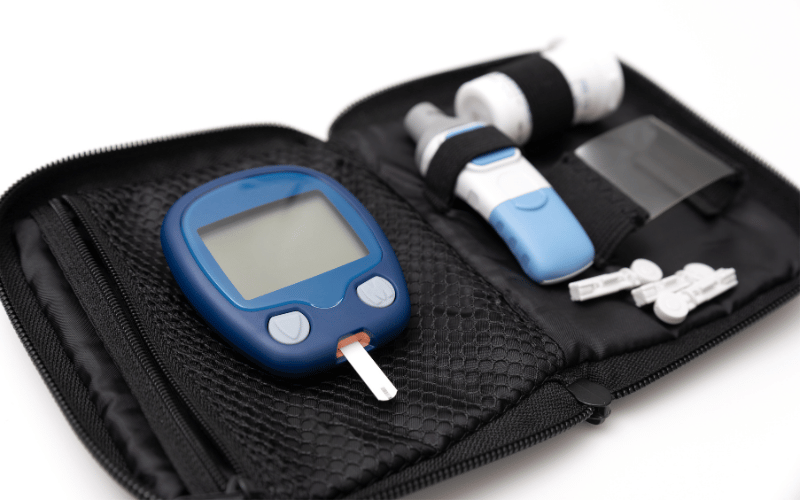
Regular blood sugar monitoring is a fundamental aspect of managing type 2 diabetes. It provides critical information about how well diabetes is being controlled and how different factors like diet, exercise, and medication affect blood sugar levels.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) involves using a blood glucose meter to check levels at various times during the day. This can help identify patterns and trends, informing decisions about diet, exercise, and medication. For those on insulin or certain oral diabetes medications, SMBG is crucial in preventing both high and low blood sugar levels.
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are another option. These systems use a small sensor placed under the skin to measure glucose levels in interstitial fluid. CGM provides real-time data on glucose levels, trends, and patterns over the course of days, offering a more comprehensive view than traditional SMBG.
Understanding and interpreting blood sugar readings are vital. Levels can fluctuate based on factors like food intake, physical activity, stress, illness, and medications. Learning to interpret these readings helps in making informed decisions about lifestyle and treatment.
However, blood sugar monitoring is not just about collecting data. It’s about using this information to make meaningful changes in diabetes management. This might involve adjusting diet, increasing physical activity, or discussing medication changes with a healthcare provider.
Effective blood sugar monitoring is a cornerstone of diabetes management. It empowers individuals with diabetes to take an active role in their care, helping to maintain optimal blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. (7)