Symptoms
Scarlet fever has a short incubation period of 1-5 days before the first symptoms appear. The clinical signs of this infection are very characteristic and include:
- A sudden high fever (up to 104°C / 40°C), leading to chills.
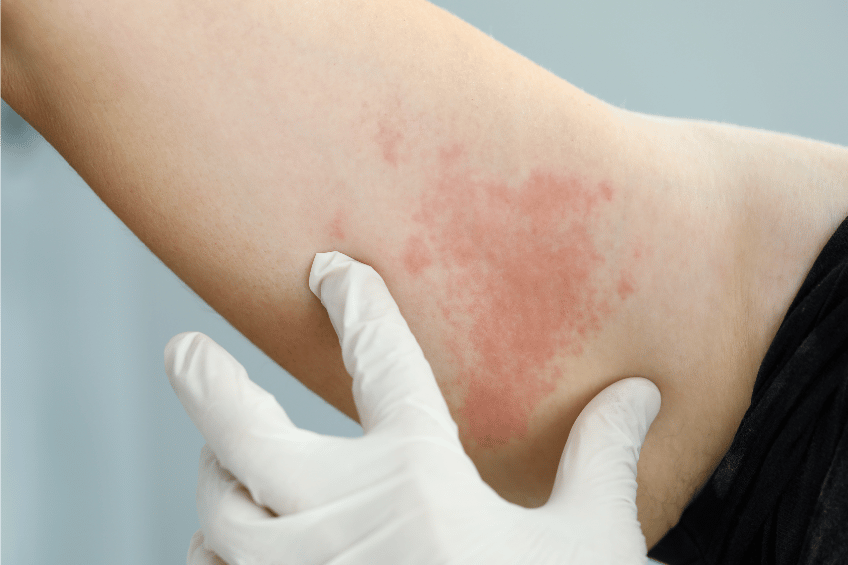
- A few days later, a red coloration of the skin (exanthema) starts on the chest and on the limbs (upper thighs, shoulders), before spreading to the whole body (except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet). Fold areas are particularly affected. The skin is dry, rough, burning with dark red spots.
- Itchy skin, that feels like sandpaper.
- Flushed red face, but pale around the mouth. The flushed face may appear more ‘sunburnt’ on darker skin.
- Red coloring of the mucous membranes (exanthema) in the throat. The tongue is first covered by a white coating. It peels off after 1-2 days, then becomes red and swollen from the 5th day and takes on a “strawberry tongue” appearance within a few days.
- Inflammation of the throat and tonsils causing a strong sore throat. This angina tends to last between 4-5 days.
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck and enlarged tonsils.
- Digestive problems such as abdominal pain and vomiting.
- Headaches.
- Heart problems such as increased heart rate (tachycardia).
After 7 days:
- The redness of the tongue disappears.
- The rash on the body disappears.
- The skin begins to peel, starting with the palms of the hands and feet, as the rash fades.
Complications
Complications usually only occur if scarlet fever is left untreated. The majority of scarlet fever cases do not cause complications.
In addition to local complications from the bacterial infection (tonsil abscesses, otitis or extensive skin infection), pneumonia is also possible, but the main concern is:
- Rheumatic fever, which causes pain in the joints.
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Cardiac disorders.
- Rarely: meningitis, septicemia, toxic shock.