Problem 3. Psoriasis: A Life-Long Battle
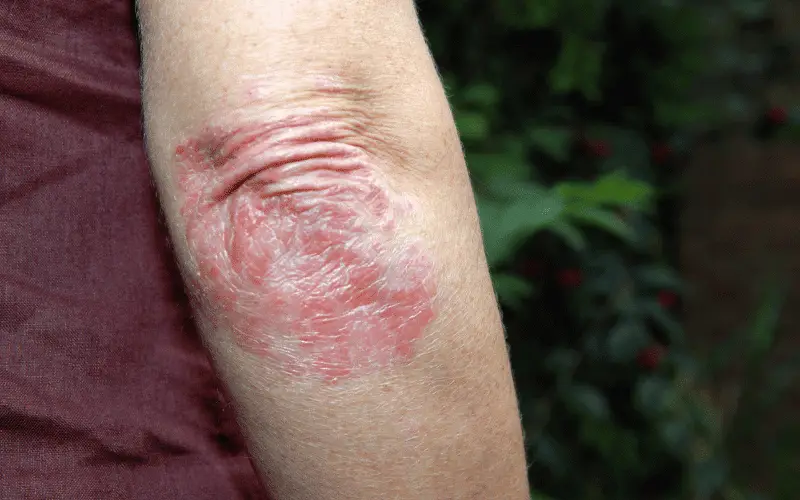
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that causes cells to build up rapidly on the surface of the skin, forming thick, scaly patches. These patches can be itchy, painful, and sometimes even crack and bleed. Psoriasis can affect any part of the body but is most commonly found on the elbows, knees, and scalp.
The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an overactive immune system. Genetics, stress, infections, and certain medications can trigger psoriasis flare-ups. While there is no cure for psoriasis, treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve the skin’s appearance.
One of the primary treatments for psoriasis is topical therapy, which involves applying medicated creams, ointments, or gels to the affected areas. Over-the-counter options include corticosteroids and coal tar, while prescription medications may include vitamin D analogues and topical retinoids. For more severe cases, phototherapy, oral medications, or biologic injections may be recommended by a dermatologist.
Lifestyle changes can also help manage psoriasis symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight, reducing stress, and quitting smoking are all crucial factors in controlling flare-ups. Additionally, incorporating a regular skincare routine, including gentle cleansing and moisturizing, can help keep the skin hydrated and reduce irritation. (3)