Problem 5. Hives: A Bumpy Ride
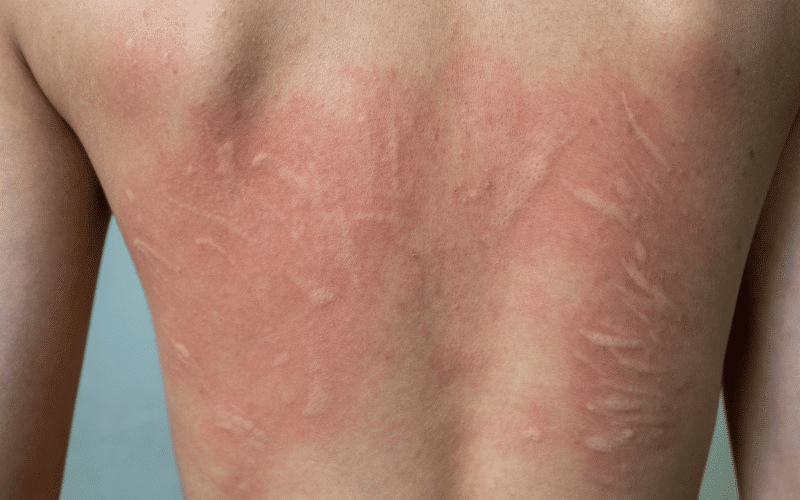
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can appear suddenly and often disappear within hours to days. They can be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergies, infections, stress, and exposure to heat or cold. Hives can range in size from small spots to large, interconnected patches and can be localized or widespread on the body.
The primary treatment for hives is antihistamines, which help to reduce itching and inflammation. Over-the-counter options, such as cetirizine, loratadine, and fexofenadine, can provide relief for mild to moderate cases. In more severe or chronic cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger antihistamines or other medications, such as corticosteroids, to help control the immune system’s response.
In addition to medication, it’s essential to identify and avoid potential triggers for hives. This may involve keeping a symptom diary to identify patterns and potential causes, undergoing allergy testing, or making lifestyle changes to reduce stress and exposure to allergens. Applying cool compresses to the affected areas can also help to alleviate itching and discomfort.
For those with chronic hives, seeking support from online forums, support groups, or a mental health professional can help manage the emotional impact of living with this condition. By working closely with a healthcare professional and adopting a proactive approach, you can minimize the frequency and severity of hives outbreaks. (5)