5. Bone Marrow Transplantation – A Transformative Approach
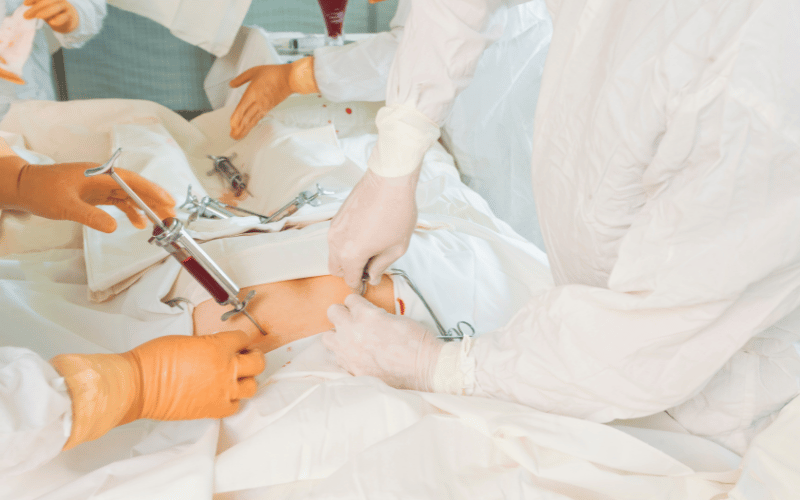
Bone marrow transplantation offers a potential cure for certain types of neutropenia, especially those stemming from bone marrow disorders. This procedure involves transplanting healthy bone marrow cells from a donor into the patient. The goal is to replace malfunctioning marrow with healthy cells, thus restoring normal blood cell production, including neutrophils.
Not every patient with neutropenia is a candidate for bone marrow transplantation. Eligibility depends on various factors, including the underlying cause of neutropenia, the patient’s overall health, and the availability of a suitable donor. This assessment is crucial to ensure the best possible outcomes from the transplantation.
Bone marrow transplantation is a complex and intensive process. It involves preparatory treatments like chemotherapy or radiation to eradicate the patient’s existing bone marrow, followed by the transplantation itself. Recovery from this procedure can be lengthy and requires close medical supervision. Patients are monitored for complications like graft-versus-host disease and infections.
After a bone marrow transplant, patients enter a critical phase of recovery. They require ongoing care to prevent infections and manage any complications. This includes regular monitoring, medication management, and supportive care. The focus during this period is on ensuring the successful integration of the transplanted marrow and the restoration of healthy blood cell production. (5)