Introduction: Navigating the Complexities of Adult Chickenpox
Chickenpox, while commonly associated with childhood, presents a unique and often more serious set of challenges when it occurs in adults. Known medically as varicella, this contagious disease is characterized by a set of symptoms that can lead to significant discomfort and potential complications if not properly managed. The adult immune system responds differently to the varicella-zoster virus, the pathogen responsible for chickenpox, making the symptoms and risks vary from those in children.
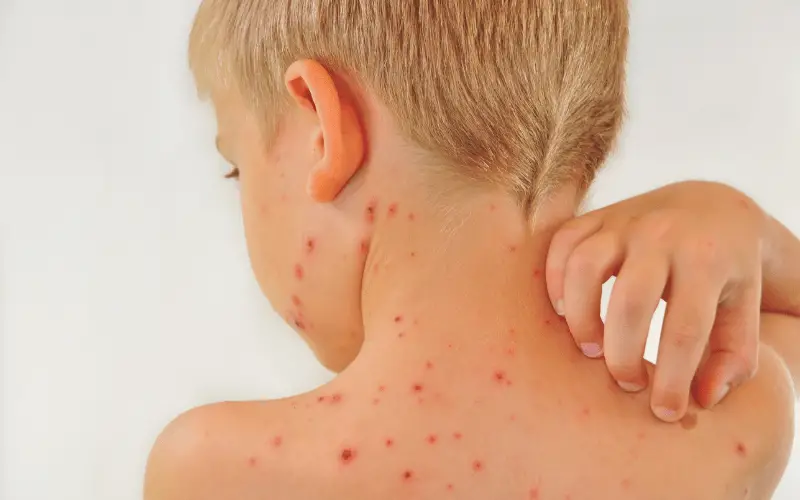
The initial encounter with the varicella-zoster virus typically occurs during childhood, resulting in chickenpox. However, when an adult contracts the virus, either due to not having it in childhood or through a weakened immune response, the symptoms can be more severe. This severity is partly because the adult immune system, having matured, reacts more intensely to the virus. Consequently, adults with chickenpox often experience more pronounced symptoms and a higher risk of complications compared to their younger counterparts.
Understanding the symptoms of chickenpox in adults is crucial for early detection and treatment. This knowledge not only helps in managing the disease effectively but also in reducing the risk of transmitting it to others, particularly to those who have never had chickenpox or have a weakened immune system. Chickenpox is highly contagious and can easily spread through direct contact or respiratory droplets from an infected person.
Moreover, the societal and economic impacts of adult chickenpox should not be underestimated. Adults suffering from the illness often require time off from work or their daily responsibilities, which can lead to significant disruptions in their personal and professional lives. Therefore, awareness and understanding of the symptoms and management strategies are vital for adults, especially those who have never been vaccinated or exposed to the virus.
In the following sections, we will explore the ten primary symptoms of chickenpox in adults, delving into the specifics of each symptom, its impact, and the best practices for managing it. This information aims to equip adults with the knowledge needed to navigate through the illness effectively, should they find themselves or someone close to them affected by adult chickenpox.
Symptom 1: Fever

The fever associated with adult chickenpox is not just a trivial rise in body temperature. It typically begins as a low-grade fever and gradually escalates, often surpassing 101°F (38.3°C). This fever serves as the body’s initial defense against the varicella-zoster virus, signaling the start of the immune response. Adults often experience accompanying symptoms like chills and sweats, which fluctuate as the fever spikes and subsides.
In addition to its physical toll, the fever affects an individual’s daily routine. Adults with chickenpox often find themselves needing to take time off work or other responsibilities due to the debilitation caused by the fever. The prolonged nature of this fever, which can last several days, further complicates matters, draining the individual’s energy and contributing to overall discomfort.
Managing this fever is crucial for comfort and recovery. Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be effective in reducing the fever, but it’s essential to avoid aspirin due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome. Besides medication, practical measures such as staying hydrated and resting can aid in managing fever symptoms.
The fever’s impact on adults is not to be underestimated. Unlike in children, where the fever tends to be milder and of shorter duration, adults can experience a more intense and prolonged feverish state. This intensity can be alarming, but it’s important to remember that it is a normal part of the body’s process in fighting the infection.
As the fever begins to subside, it often signals the progression of the disease to more visible symptoms, such as the characteristic chickenpox rash. The resolution of the fever is a positive sign, indicating that the body is starting to overcome the virus. However, it’s important to continue monitoring other symptoms and seeking medical advice if the fever persists or other severe symptoms develop. (1)