Introduction: Navigating the Complexities of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) affects a significant portion of the population, yet it often remains under-discussed and poorly understood. This condition revolves around the Eustachian tube, a key component in the ear’s anatomy responsible for equalizing air pressure and facilitating fluid drainage.
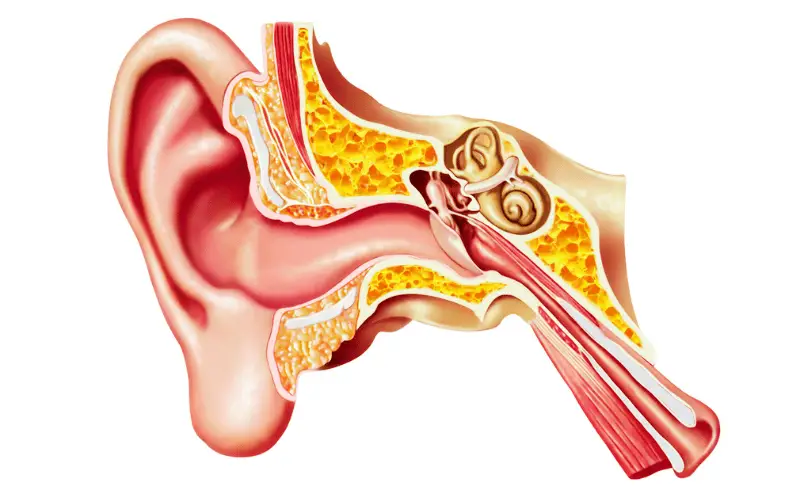
ETD occurs when this tube malfunctions, leading to a range of symptoms that can affect hearing and balance. In this introduction, we’ll delve into the essential facts about ETD, exploring its causes, symptoms, and the impact it has on everyday life. By demystifying ETD, we aim to provide valuable insights for those experiencing this condition, healthcare professionals, and anyone interested in ear health.
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx and plays a critical role in maintaining ear health. Its primary functions include regulating air pressure in the middle ear, ensuring it matches the external air pressure, and draining any accumulated fluid. This regulation is crucial for the proper functioning of the ear, particularly for maintaining balance and hearing capabilities.
While ETD primarily affects ear health, its impact extends beyond. Symptoms of ETD, such as muffled hearing, discomfort, and tinnitus, can significantly affect quality of life, leading to frustration and anxiety. For some, ETD is a temporary inconvenience, often associated with colds or allergies. However, for others, it can become a chronic issue, necessitating a deeper understanding and more complex management strategies.
ETD is a condition that touches a wide demographic, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. Its prevalence highlights the need for greater awareness and knowledge about the condition. Understanding ETD’s symptoms, causes, and potential treatments is crucial for effective management and improving the lives of those affected.
The aim of this article is to offer a detailed exploration of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. By presenting 15 key facts about ETD, we provide an informative and engaging resource that enhances understanding of this condition. This article serves as a useful tool for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge of ETD, from patients and their families to healthcare professionals seeking to broaden their understanding of ear-related conditions.
1. Eustachian Tube Anatomy: A Vital Gateway in Ear Health
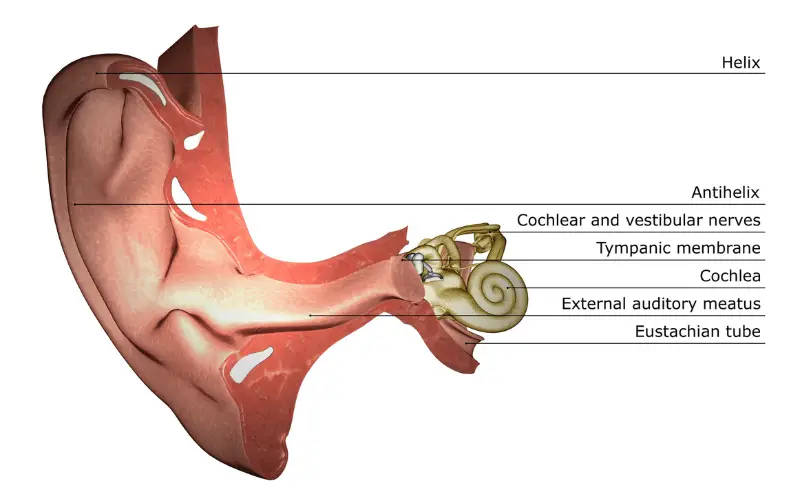
The Eustachian tube, a narrow channel, serves as a critical link between the middle ear and the nasopharynx. This tube’s primary role is to maintain equal air pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
It’s lined with mucous membrane and measures approximately 35mm in adults. Its unique structure allows it to open during activities like swallowing or yawning, thereby equalizing pressure and facilitating fluid drainage.
The Eustachian tube’s opening and closing are essential for ear health. This process balances air pressure and prevents fluid accumulation in the middle ear. This function is vital for clear hearing and maintaining balance. When the tube functions properly, it ensures the middle ear’s environment remains healthy and balanced.
Various factors can affect the Eustachian tube’s functioning. Allergies, colds, sinus infections, and even altitude changes can cause temporary dysfunction. These conditions can lead to swelling or blockage, disrupting the tube’s normal functioning. Persistent issues might indicate more chronic forms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction.
When the Eustachian tube fails to function correctly, it results in Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD). ETD can manifest in various symptoms like muffled hearing, a feeling of fullness in the ear, and discomfort. Understanding the tube’s anatomy and functionality is key to comprehending ETD’s impact on ear health. (1)