Symptom 5: Presence of Warts in the Throat or Mouth
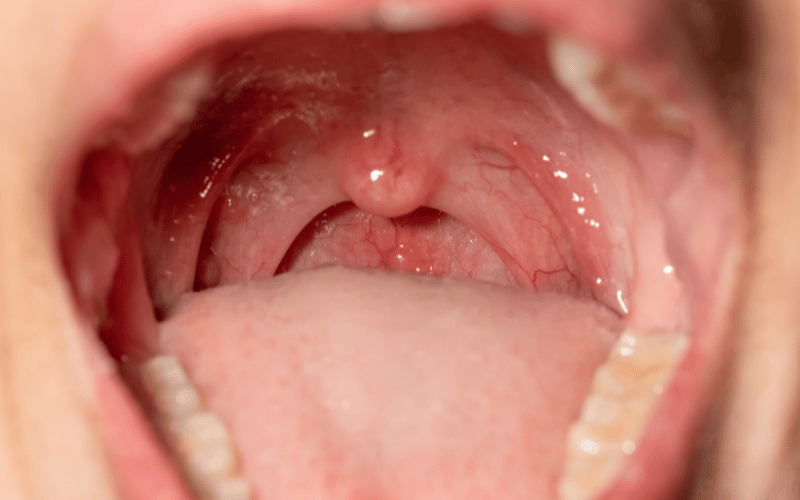
When people think of HPV, they often equate it exclusively with the genital region. This oversight can be detrimental. The Human Papillomavirus, with its vast array of strains, can find its way into the oral cavity, leading to the growth of warts in areas such as the throat and mouth. Often, oral warts are the result of engaging in intimate oral activities with an infected individual. Unlike genital warts, oral warts are not always easily identifiable due to their discrete appearance and the internal nature of some growths. Moreover, there’s a lack of general awareness about the presence of HPV in the oral region, which further obscures the recognition of symptoms.
Warts within the mouth or throat often manifest discreetly. Instead of prominent, clustered growths one might expect with genital warts, these tend to appear as small, sometimes flat, lesions. A person with oral warts might initially dismiss them as benign mouth ulcers or other common oral anomalies. Some individuals might experience symptoms like a persistently sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or even voice alterations. It’s crucial to remain vigilant and not disregard these subtle indications. Regular dental or ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) check-ups can be pivotal in early identification.
The transmission of HPV to the oral cavity often results from oral-genital contact with an HPV-infected person. This interchange means that someone with genital HPV can transmit the virus to their partner’s mouth or vice versa. The risk underscores the importance of practicing safe intimate behaviors and being aware of one’s health status and that of their partners. Vaccination, where applicable, also plays a vital role in curtailing the spread of high-risk HPV strains that can lead to warts and other complications.
Upon suspecting the presence of oral warts, seeking medical consultation becomes essential. Specialists, particularly dentists and ENT professionals, are equipped to diagnose and manage these conditions. Depending on the wart’s location, size, and strain of HPV, treatment modalities might vary. They can range from topical treatments to more invasive procedures for removal. With the advancement in medical science, numerous effective treatments have emerged to manage oral warts and reduce potential complications.
Oral warts, though less discussed than their genital counterparts, demand equal attention. Their sneaky nature, combined with the potential for complications, makes them a health concern not to be overlooked. Regular medical check-ups, safe intimate practices, and an awareness of HPV’s reach can aid in both prevention and early intervention. (5)