Introduction: What is Hairy Leukoplakia?
Hairy leukoplakia is a condition that primarily affects the mouth, particularly the tongue’s sides. It’s named for its distinct appearance, resembling white, hairy patches. Often linked with a compromised immune system, it serves as a sign of more severe underlying issues, especially in those with HIV/AIDS.
The intriguing aspect of this ailment is its relation to the Epstein-Barr virus, a common virus that most people encounter at some point in their lives. However, not everyone who has been exposed to this virus will develop hairy leukoplakia. Those who do are usually dealing with immune suppression, often due to HIV, but sometimes as a result of medications or other conditions.
While hairy leukoplakia is benign and non-contagious, it can be a source of discomfort and concern for many. The distinctive patches can affect one’s quality of life, from the taste of food to feelings of self-consciousness. The condition, while not life-threatening on its own, signals the need for individuals to assess their broader health circumstances.
Knowledge is the first step in addressing any health issue. Being familiar with the symptoms and manifestations of hairy leukoplakia is the beginning of the journey. With the right information, patients can approach their healthcare providers confidently, ensuring they receive the care they need.
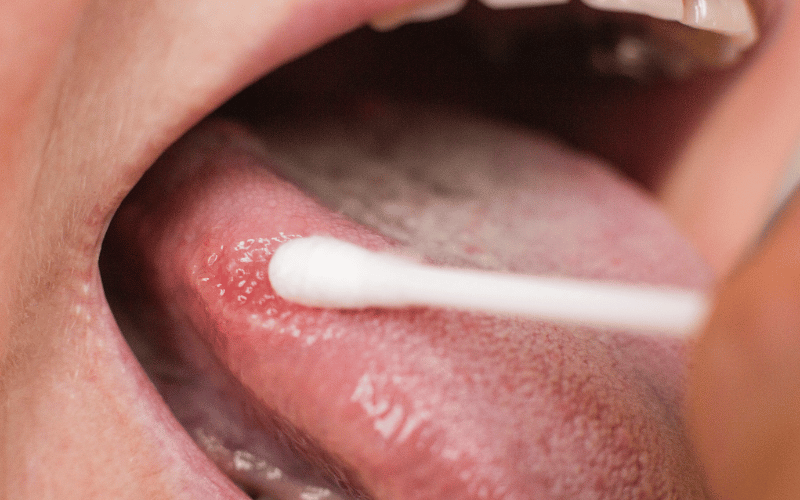
Symptom 1: White or Grayish Patches
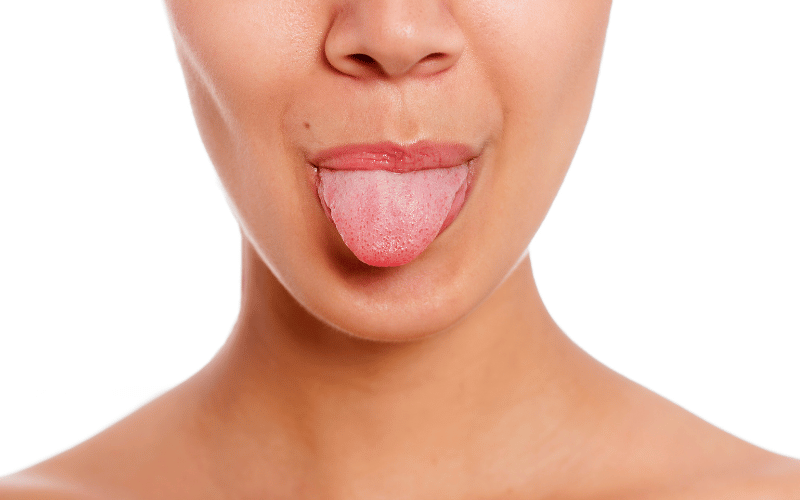

One of the hallmark signs of hairy leukoplakia is the appearance of white or grayish patches, predominantly on the sides of the tongue. These patches aren’t just a cosmetic concern; they’re a key indicator of the condition. They contrast starkly with the typical pink hue of a healthy tongue, making them easily noticeable.
The texture of these patches is also distinct. Unlike some other oral issues, the surface of these patches is often rough and corrugated. This rugged texture can sometimes make the eating experience a bit uncomfortable for the individual.
Not to be confused with other white lesions in the mouth, these patches stand out because they’re resistant to being scraped off. This is a significant differentiator from conditions like oral thrush, where the white patches can be easily removed. Moreover, these patches aren’t just isolated to the tongue. In some cases, they can appear elsewhere in the mouth. However, the tongue’s lateral sides remain the most common site. (1)