Fact 7: The Critical Role of Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
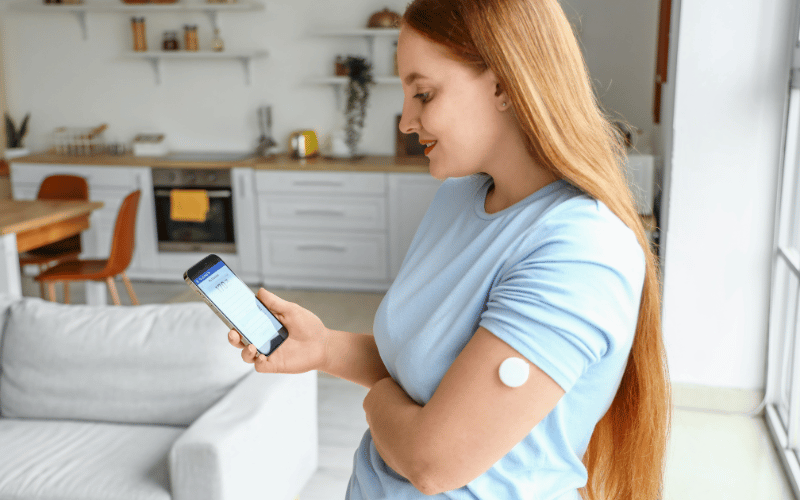
Regular blood sugar monitoring is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. It provides critical information about how well the treatment plan is working and helps identify patterns and trends in blood sugar levels. This data is invaluable in making informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
Blood sugar monitoring can be done through traditional fingerstick tests or with continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. Fingerstick tests provide a blood sugar reading at a specific point in time, while CGM systems offer real-time continuous tracking. CGM systems are particularly beneficial for gaining a more comprehensive understanding of blood sugar patterns and for individuals who experience frequent hypoglycemia or have difficulty maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
The frequency and timing of blood sugar monitoring can vary depending on the individual’s treatment plan, type of diabetes, and lifestyle factors. Some people may need to check their blood sugar several times a day, while others may do so less frequently. The monitoring schedule should be tailored to each individual’s needs and adjusted based on changes in treatment, activity levels, and eating habits.
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in guiding and interpreting blood sugar monitoring. They can help set target blood sugar ranges, interpret the results, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Regular check-ins with healthcare providers are essential to ensure that the monitoring approach remains effective and aligned with the individual’s health goals.
Educating patients about the importance and techniques of blood sugar monitoring is vital. This includes teaching how to use monitoring devices correctly, how to interpret the results, and how to respond to high or low blood sugar readings. Empowered and informed patients are more likely to engage in effective self-management of their diabetes, leading to better health outcomes. (7)