6. The Threat of Thrombosis: Understanding Clot Risks in PV
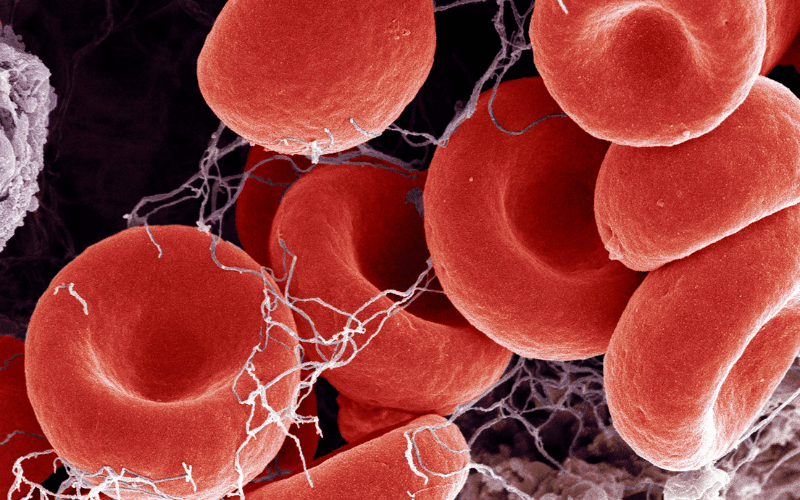
One of the most significant threats facing individuals with PV is the risk of thrombosis, which is the formation of blood clots. These clots can occur in veins and arteries and can lead to serious health issues such as stroke or heart attack, potentially affecting life expectancy.
The increased red blood cell mass in PV patients means their blood is thicker and more prone to clotting. This necessitates a vigilant approach to monitoring and treatment to minimize the risk. Aspirin is often prescribed to reduce blood stickiness and help prevent clots.
Recognizing the signs of a blood clot is crucial. Symptoms such as swelling, pain, redness, or warmth in a limb, shortness of breath, or chest pain require immediate medical attention. Early intervention can be life-saving.
Regular check-ups can help monitor blood thickness and clotting factors. Keeping these in check is a continuous effort but is essential for preventing thrombotic events, preserving health, and prolonging life in PV patients. (6)