2. Dysphagia: When Swallowing Becomes a Challenge
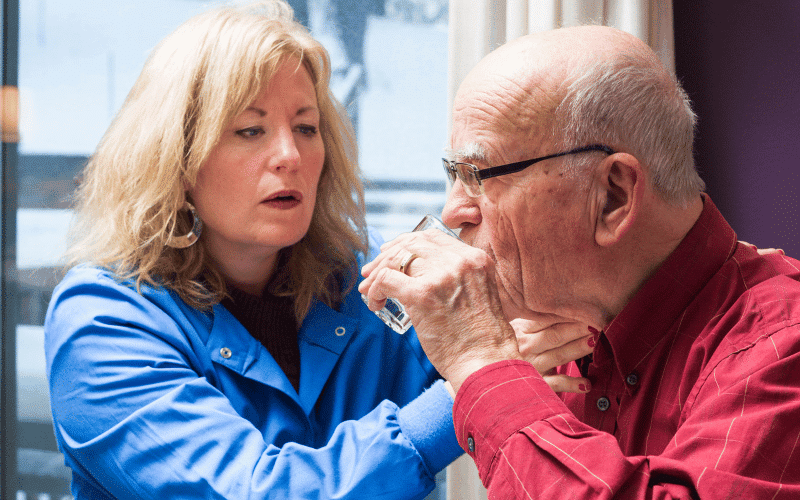
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, might not be the first symptom to come to mind when one thinks of pseudobulbar palsy, but it is a frequent and significant problem for many individuals with this condition. When the muscles involved in the swallowing process become weak due to pseudobulbar palsy, it can lead to dysphagia.
Swallowing is a complex process involving numerous muscles and nerves, and disruption at any stage can lead to dysphagia. In pseudobulbar palsy, damage to the nerve pathways controlling these muscles leads to a lack of coordination, causing difficulty swallowing.
Dysphagia has far-reaching implications, from physical health risks to emotional and psychological distress. Physically, difficulties with swallowing can result in malnutrition, weight loss, and dehydration. Additionally, it raises the risk of aspiration, where food or liquid goes down the wrong pipe into the lungs, leading to serious infections like pneumonia.
Addressing dysphagia is vital for ensuring adequate nutrition and reducing the risk of complications. Strategies can include changes in diet, like switching to softer or pureed foods, or altering eating habits to make swallowing easier.
In severe cases, a feeding tube may be required to ensure the individual receives sufficient nutrition. Speech and language therapists can also offer exercises and techniques to improve swallowing control and coordination. (2)