9. Tracheomalacia and Sleep-Related Challenges
Sleep-related challenges are a significant concern in individuals with tracheomalacia, impacting both quality and quantity of sleep. Understanding and addressing these issues is crucial for overall health and well-being.
The weakened trachea in tracheomalacia can lead to increased respiratory issues during sleep. This is particularly evident in positions like lying flat, where gravity can exacerbate the tracheal collapse, leading to obstructed breathing, snoring, and even sleep apnea.
Children with tracheomalacia may show signs of disturbed sleep, such as frequent awakenings, restlessness, or difficulty in falling asleep. These disruptions can affect their behavior and development, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and intervention.
In adults, poor sleep quality due to tracheomalacia can lead to daytime fatigue, reduced concentration, and impaired cognitive function. Chronic sleep deprivation can also exacerbate other health issues, creating a cycle of worsening health and sleep quality.
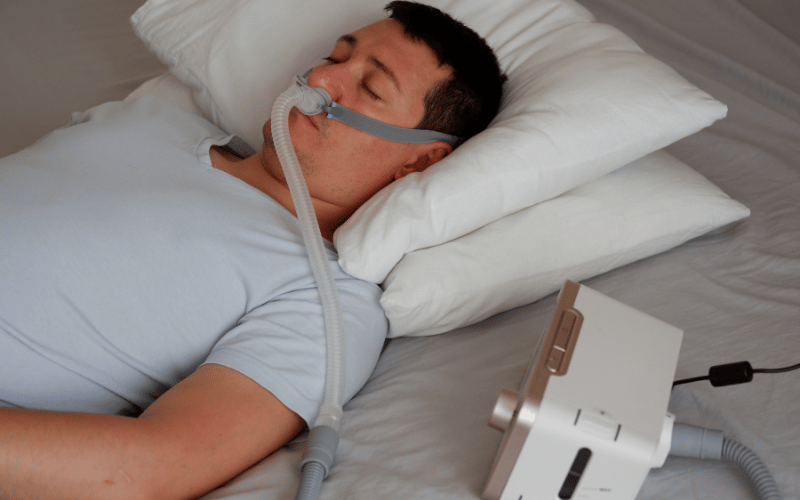
Management of sleep-related issues in tracheomalacia often involves a combination of positional therapy, where sleeping in a more upright position can alleviate symptoms, and the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices in more severe cases.
Addressing sleep challenges in tracheomalacia is a vital component of comprehensive care. It requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving pulmonologists, sleep specialists, and, in the case of children, pediatricians, to ensure effective management and improved quality of life. (9)