Cause 10. Severe Burns or Trauma: The Stress Response and Its Impact on Potassium Levels
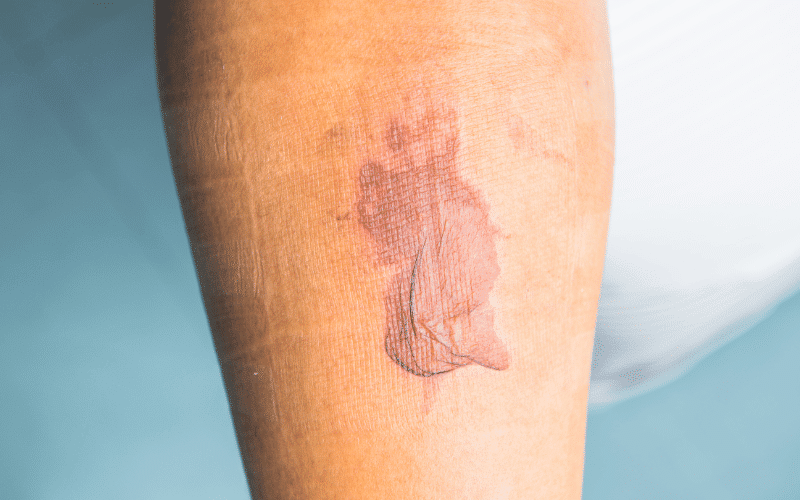
Severe burns, trauma, or major surgeries can lead to a dramatic drop in potassium levels due to the body’s stress response. In these situations, the body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause a rapid shift of potassium from the bloodstream into the cells. This results in a temporary decrease in blood potassium levels, potentially leading to hypokalemia.
Furthermore, extensive burns can lead to significant potassium loss through damaged skin and increased fluid requirements. This, combined with the body’s stress response, can exacerbate hypokalemia in burn victims.
Treatment for trauma or burn-related hypokalemia focuses on addressing the underlying cause and providing appropriate medical care for the injury or surgical procedure. Potassium supplementation and a potassium-rich diet may be recommended to help restore potassium levels. In severe cases, intravenous (IV) potassium administration may be necessary to correct life-threatening hypokalemia. (9)