Introduction: Demystifying Bronchiectasis – A Deep Dive into Its Core
Bronchiectasis, a chronic respiratory condition often eclipsed in the broader conversation about lung health, demands a closer examination due to its significant impact on those affected. This disease, characterized by irreversible widening of the bronchi – the major air passages in the lungs – leads to various symptoms that can severely affect one’s quality of life. Understanding bronchiectasis is not just about recognizing its medical definition; it’s about comprehending how it affects individuals daily, the challenges in diagnosing it, and the importance of early intervention for effective management.
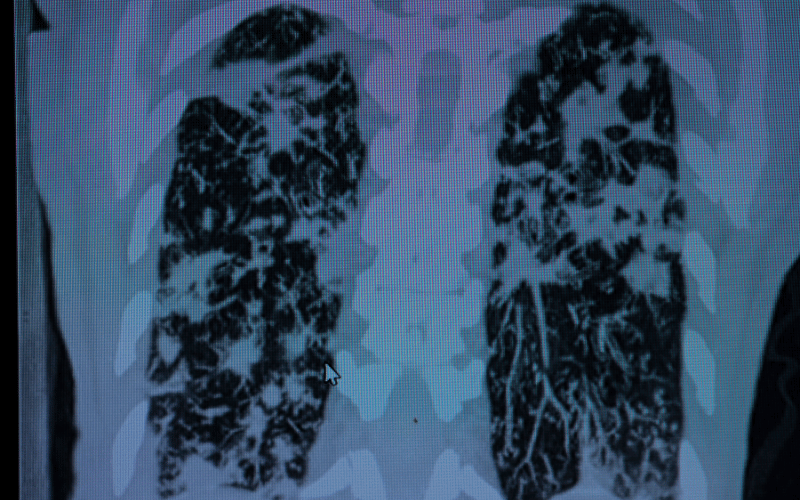
At its core, bronchiectasis is a condition marked by a cycle of lung damage, infection, and inflammation. This cycle begins when the airways become damaged due to an infection or other lung condition, leading to a widening of the bronchi. This widening disrupts the normal clearing mechanisms of the lungs, causing mucus to accumulate. The presence of this excess mucus then becomes a breeding ground for bacteria, leading to recurrent infections. These infections cause further inflammation and damage, perpetuating the cycle.
The challenge in managing bronchiectasis lies in its varied symptomatology and the fact that its symptoms often overlap with those of other respiratory conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. This overlap can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis, impacting the effectiveness of treatment and management strategies. Therefore, a deep understanding of the symptoms specific to bronchiectasis is crucial for healthcare providers and patients alike. Additionally, the impact of bronchiectasis extends beyond the physical symptoms. The chronic nature of the disease, coupled with frequent exacerbations, can lead to significant psychological stress and a decrease in quality of life. Patients often experience anxiety and depression due to their illness, which can further complicate treatment and management. Recognizing and addressing these psychological aspects is a critical component of comprehensive care.
The aim of this article is to provide an in-depth look at bronchiectasis, focusing on its symptoms, diagnosis, and management. By the end of this piece, readers should have a thorough understanding of the condition, empowering them to seek appropriate care and support if needed. The journey through understanding bronchiectasis starts with its symptoms – the primary indicators that signal the presence of this complex respiratory condition.
Symptom 1: Persistent Cough

A persistent cough in bronchiectasis is more than a mere annoyance; it’s a chronic, often debilitating symptom. This cough, unlike those accompanying a common cold, lingers for weeks, months, or even longer. It’s characterized by its persistence and the ability to produce mucus, which can be clear, yellow, greenish, or even blood-tinged. The nature of the cough in bronchiectasis is a reflection of the chronic inflammation and infection in the airways, making it a key indicator of the disease.
The relentless nature of this cough significantly impacts daily life. It can disrupt sleep, interfere with social interactions, and even cause physical discomfort. The need to constantly clear the throat can be both physically tiring and socially embarrassing, leading to a decrease in quality of life. For many, this persistent cough becomes a defining aspect of living with bronchiectasis, affecting both physical and mental well-being.
Managing this symptom involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Airway clearance techniques, such as postural drainage and chest physiotherapy, play a crucial role in helping to clear mucus. Bronchodilators and inhaled steroids can also be prescribed to reduce inflammation and open up the airways. Staying hydrated and avoiding irritants like smoke can further help in managing this symptom effectively.
If left unmanaged, a persistent cough can lead to complications such as chest pain, muscle soreness, and even rib fractures in severe cases. The continuous strain of coughing can exert significant pressure on the chest and abdominal muscles, leading to discomfort and potential injury.
This symptom, while challenging, is manageable with the right approach. Timely intervention and a tailored management plan can significantly reduce the impact of a persistent cough, improving the overall quality of life for individuals with bronchiectasis. It’s essential to not dismiss this symptom as a mere inconvenience but to recognize it as a vital indicator of lung health requiring attention and care. (1)