Treatment and prevention
Once you have a blockage, it’s generally there to stay. But there are treatments that prevent its progression and help to avoid serious consequences.
A healthy lifestyle and the treatment of risk factors such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and diabetes help to stop or slow the progression of atherosclerosis.
Prevention:
- Quitting smoking;
- Strict control of blood pressure;
- Management of dyslipidemia;
- Diabetes control;
- Maintaining regular physical activity;
- Dealing with excess weight.

Depending on the degree of severity of the arterial narrowing, the drug treatment may be different:
- Platelet antiaggregants, the purpose of which is to prevent the formation of clots in the bloodstream and contact with the injured arterial wall;
- Statins, always combined with a balanced and low-fat diet, the purpose of which is to correct possible dyslipidemia;
- Antihypertensive treatments that depend on the degree of high blood pressure,

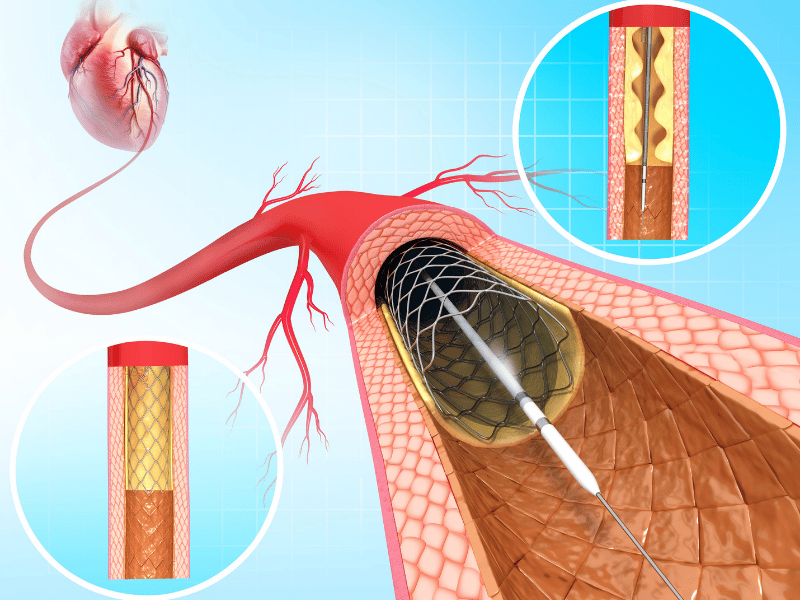
Treatments may also include angioplasty (the dilation of narrowed blood vessels), an implantation of a stent, and sometimes surgery.
Atherosclerosis can affect the entire arterial territory. It is the consequence of a set of predisposing or acquired factors throughout one’s life. Medical treatment is based on prevention, risk factor control, and the introduction of certain medications. Follow-ups should be regular and thorough.
Stay healthy and never hesitate to seek medical advice!