3. The Impact of Body Weight and BMI: Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes
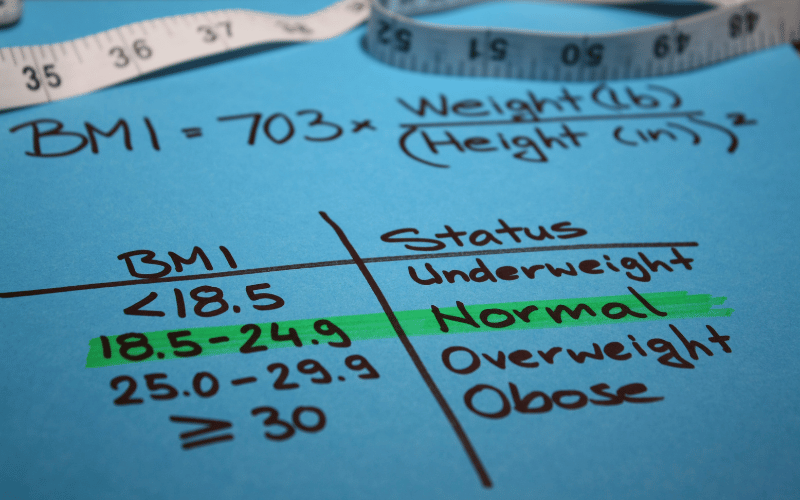
The relationship between body weight, Body Mass Index (BMI), and the risk of gestational diabetes is a topic of paramount importance. This chapter discusses how excess weight and a high BMI can significantly increase the likelihood of developing this condition during pregnancy.
Excess body weight, especially obesity, has been linked to insulin resistance. This resistance impairs the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, a key factor in the development of gestational diabetes. The higher the BMI, the greater the risk, making weight management an essential consideration for women planning to conceive.
BMI is a useful tool in assessing this risk. It provides a quick snapshot of where one’s weight stands in relation to their height. However, it’s crucial to understand that BMI is not the only measure; body composition and distribution of fat also play significant roles.
What makes weight and BMI notable risk factors is that unlike genetics or age, they are modifiable. Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthier diet and engaging in regular physical activity, can significantly reduce the risk associated with a high BMI.
Finally, it’s not just about the numbers on the scale. The quality of diet and the type of physical activity are equally important. A focus on overall health and well-being, rather than just weight loss, is key in managing the risk of gestational diabetes related to body weight and BMI. (3)