Vitamin D Deficiency.
Vitamin D plays many important roles in the body. Primarily produced under the effect of sunlight, vitamin D provides many health benefits, from bone strength and muscle maintenance to strengthening the immune system. Moderate daily exposure to the sun, as well as a varied and balanced diet, are necessary to avoid vitamin D deficiency. Its symptoms can then have various consequences on the body.
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that can either be provided by food, or be synthesized in the human body under the action of UVB (Ultraviolet B) rays during exposure to the sun.
There are two types of vitamin D found in food:
- Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol): which comes from foods of plant origin
- Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol): which comes from foods of animal origin or is synthesized in the skin by the action of ultraviolet light on cholesterol following exposure to the sun
The body can also get vitamin D from supplements that are absorbed through the intestine. Vitamin D plays a major role in the assimilation and fixation of calcium and phosphorus in the bones, ensuring the strength of the skeleton. It helps the body’s immune system to fight viruses and bacteria (in case of cold, allergy, illness…). It is also involved in hormonal regulation. It preserves the brain from premature decline in cognitive and intellectual functions and certain mental illnesses. Finally, it helps to fight against the development of certain cancers and cardiovascular diseases.

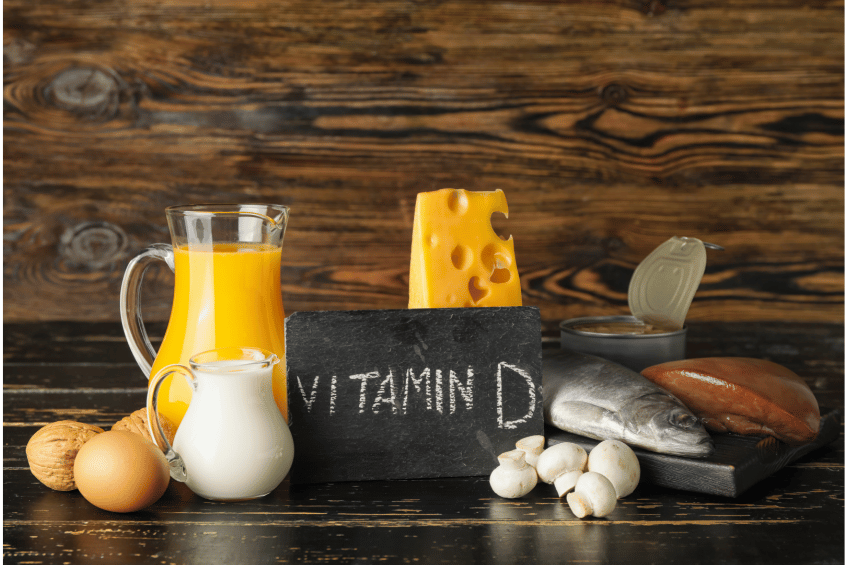
Sources of Vitamin D.
There are several ways to meet daily vitamin D needs:
-
- Exposure to the sun: by exposing yourself to the sun for 15 to 20 minutes in the late morning or afternoon, you can ensure that your body has a sufficient daily intake of vitamin D. However, in winter, or in certain regions with little sunshine, it is highly possible to have insufficient levels of this vital vitamin.
- Food supplements: vitamin D can also be ingested through medicine and food supplements of different concentrations and compositions.
- Eating foods rich in vitamin D, such as:
- Dark chocolate
- Egg yolk
- Oily fish, such as herring, sardines, salmon and mackerel
- Certain mushrooms, such as chanterelles, ceps and morels
- Dairy products fortified with vitamin D
- Butter and margarines
- Breakfast cereals fortified with vitamin D
- Offal/Variety meats (especially liver)
- Red meat

People at risk of developing Vitamin D deficiency.
The need for vitamin D is individual and depends on a variety of different parameters. However, there are certain groups that have an increased need for vitamin D:
-
- The elderly: the synthesis of this vitamin is much slower, even if there is a sufficient supply of UV radiation.
-
- Pregnant women: the increased need is due to the fact that the embryo also needs vitamin D to develop.
- Infants: because the vitamin D content in breast milk is low and infants should not be exposed to direct sunlight.
- The color of the skin: the lighter the skin, the faster the production of vitamin D. This is a particular problem for people with dark skin who live in northern latitudes with little sunlight. They are more likely to develop seasonal depression.
- Certain kidney and liver diseases: including chronic kidney failure, severe liver disease and hyperthyroidism.
- People who do not eat fish or dairy products.
- Obesity is also a risk factor: vitamin D accumulates in adipose tissue from which it cannot be released into the bloodstream – in this case there is a deficiency.
- People taking high doses of medication for rheumatoid arthritis (dexamethasone) or anti-epileptic and anti-viral drugs which may interfere with the absorption of vitamin D.
- People who have been bedridden for a while or who don’t get enough outdoors and suffer from a lack of sunlight.
- Those who usually wear clothes that cover up most of their skin when outdoors.
- Women during menopause.
- Certain digestive problems causing malabsorption, including Crohn’s disease, inflammatory bowel disease, cystic fibrosis, and celiac disease. They can affect the intestine’s ability to absorb vitamin D from food.

It’s important to remember that even if none of the above applies to your particular situation, no one is immune to vitamin D deficiency, especially in winter.
What is the normal level of vitamin D?
A level of 20 ng/ml to 50 ng/ml is considered adequate for healthy people. Deficiency is defined as a level below 12 ng/ml.
How much vitamin D should you consume each day?
According to NHS guidelines, children from the age of 1 and adults need 10 micrograms of vitamin D a day. This includes pregnant and breastfeeding women, and people at risk of vitamin D deficiency. Babies up to the age of 1 need 8.5 to 10 micrograms of vitamin D a day.
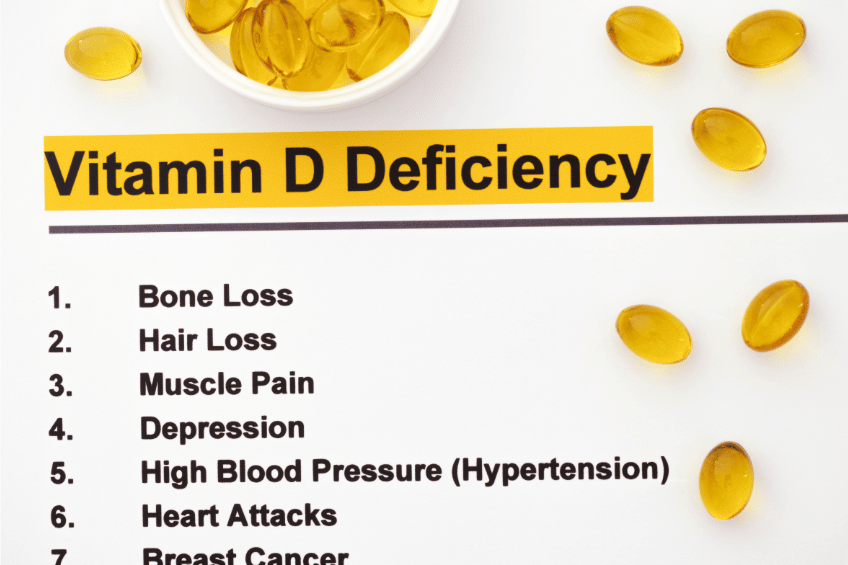
What are the consequences of Vitamin D deficiency?
- Vitamin D deficiency leads first and foremost to bone risk.
- Severe vitamin D deficiency can lead to rickets in infants and young children. Rickets is a childhood disease characterized by impeded growth and deformity of the long bones. The earliest sign of vitamin D deficiency is craniotabes, abnormal softening or thinning of the skull.
- In adults, it can lead to softening of the bones (osteomalacia) or spontaneous fractures (osteoporosis).
- Poor cell division.
- Increased risk of cancer (mainly breast and colorectal cancer).
- Weakened immune system: this can lead to diseases such as Type 1 diabetes, Multiple sclerosis, Rheumatoid arthritis and frequent illness or infections.
- Depression and mood swings, as the production of serotonin, the natural “feel-good hormone”, is slowed down.
- High blood pressure.
- Complications during pregnancy .
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency.
Vitamin D is an essential vital element, which, when it is lacking, can lead to many dysfunctions. In adults, this deficiency develops over the long term. Symptoms are often diffuse. It can be general fatigue, constant lower mood, lack of tone or muscle weakness. You may have to help yourself with your hands when getting up or have difficulty climbing stairs.
Examples of symptoms:
-
- Fatigue.
- Constant lowered mood; an impact on morale happens because serotonin is directly linked to vitamin D.
- Anxiety.
- Muscular weakness: vitamin D plays an essential role in maintaining muscle mass.
- Widespread pain.
- Lack of tone in the muscles.
- Cramps.
- Difficulty walking.
- Bone pain.
- Bone fractures ( especially in those over 65).
- A tingling sensation in the limbs.
- Hair loss, as the deficiency weakens hair follicle productivity.
- Circulatory problems.
- Impaired wound healing.
- Tension headaches.
- Dry skin: Abnormally dry skin can be caused by a vitamin D deficiency. The latter is involved in the hydration of the skin and tissues.
- In more serious cases, a prolonged and acute deficiency in vitamin D can weaken the bones (osteoporosis), or soften them (osteomalacia).

Diagnosis.
In order to detect vitamin D deficiency, blood tests are performed. The levels of other vitamins or hormones related to the vitamin may also be affected. However, it can be difficult to determine whether the level is representative of a deficiency as it can be influenced by seasonal changes, sun exposure, age, and BMI, among other things.
What to do in case of deficiency?
First, it is all about following a balanced diet. It is advisable to preventively consume foods rich in vitamin D. It is also necessary to expose your skin to the sun for 15 to 30 minutes a day during the brightest time, of course, taking care to avoid damage caused by the sun by covering up and using SPF.
Those most at risk for vitamin D deficiency can benefit from taking vitamin D supplements. Treatment involves taking high doses of vitamin D daily, usually orally, for about 1 month. After a month, the dose is usually reduced gradually to the usual recommended dose.
In breastfed children, it is especially important to start vitamin D supplements at birth, because breast milk contains little vitamin D. Infants are given supplements until 6 months of age, when their diet becomes more varied.

Vitamin D Supplementation.
Vitamin D supplementation should only be taken in the event of a proven deficiency and in agreement with the doctor. An overdose of vitamin D cannot occur naturally, either through excessive exposure to the sun or through an abundant consumption of food containing vitamin D. An overdose is possible following the intake of food supplements or preparations with high doses of vitamin D.
It is dangerous to ingest more than 100 micrograms (4,000 IU) of vitamin D per day for a long period of time. This applies to adults, including pregnant and breastfeeding women and the elderly, and children aged 11 to 17. Children aged 1 to 10 should not have more than 50 micrograms (2,000 IU) a day. Infants under 12 months should not have more than 25 micrograms (1,000 IU) a day.
At very high doses, vitamin D causes an excess of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia) and in the urine (hypercalciuria). Too much intake can manifest itself by the following symptoms:
- Heart rhythm disorders: cardiac arrhythmias.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Weakness.
- Poor appetite.
- Weight loss.
- Fatigue.
- Headache.
- Loss of consciousness.
- In the long term, an overdose can also lead to kidney stones and kidney failure.
It is important to keep track of your vitamin D levels. Regular check-ups will help prevent serious health issues and ensure you have a happy, healthy life.
