3. Your Diet Plays a Significant Role in Potassium Levels
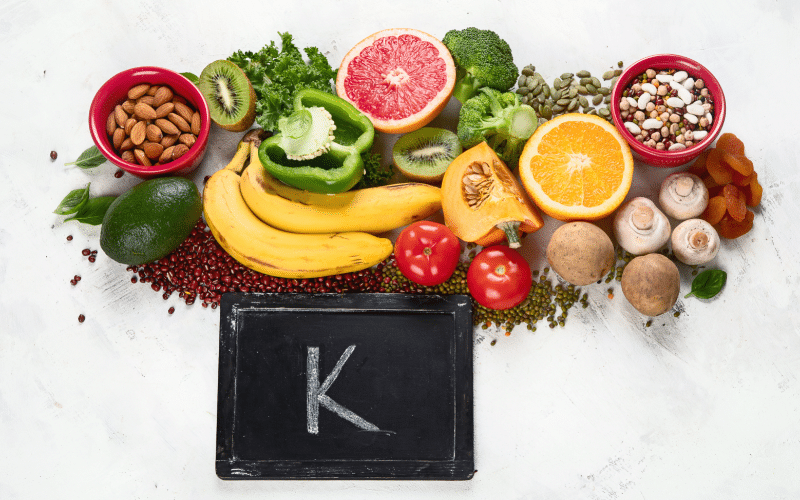
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for regulating potassium levels in the body. Potassium-rich foods include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, such as bananas, oranges, potatoes, spinach, and beans. Consuming a variety of these foods can help you achieve the recommended daily potassium intake of 2,500 to 3,400 milligrams for adults. (4)
However, it’s essential to be mindful of your potassium consumption. Consuming excessive amounts of potassium can lead to hyperkalemia, while insufficient potassium intake can cause hypokalemia. To maintain optimal potassium levels, aim for a well-rounded diet that includes the right balance of potassium-rich foods. (Related article – 20 Best Foods for a Low-Potassium Diet: Discover the Top Choices for Your Health)
It’s also important to consider that processed foods can negatively impact potassium levels. Many processed foods are high in sodium and low in potassium, which can contribute to an imbalance of these essential minerals. By focusing on a whole-foods-based diet, you can better manage your potassium levels and support overall health.