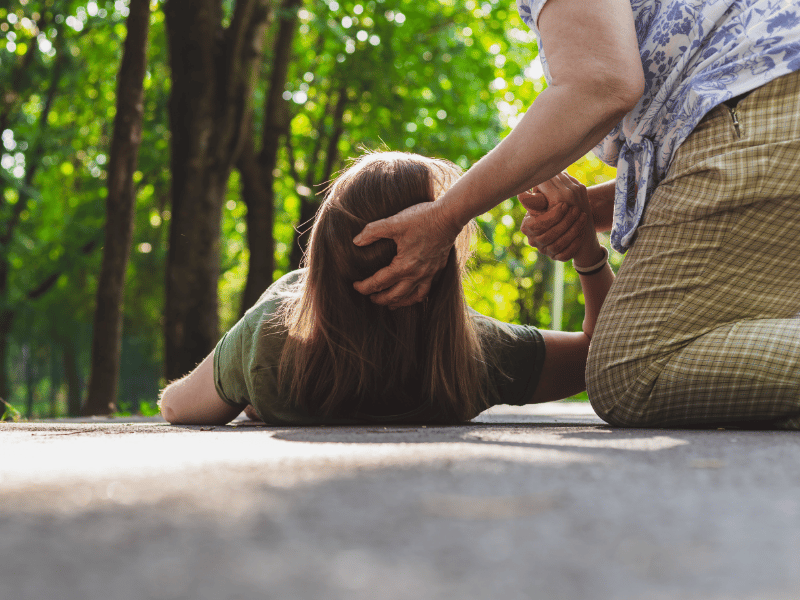
First aid
Every minute counts! The most effective treatment is possible in the first three hours after stroke onset. When the first symptoms appear, call an ambulance immediately. Describe exactly what happened so that a specialized paramedics team arrives.
- Do not drive to the hospital or let someone else drive you. Getting to hospital as quickly as possible is the key to stroke treatment. If you get to the facility by calling an ambulance, there are higher chances of being first in line to the ER and medical staff can begin life-saving treatment on the way to the clinic.
- While waiting for the ambulance to arrive, make sure there’s a flow of fresh air. Whether inside or outside, ask people to step away.
- Never try to move the person with stroke. It can be dangerous. The patient should stay where the attack occurred.
- Lift their upper body and head. It`s best to put a few pillows under them. Unfasten or remove all tight clothing and accessories to ensure easy breathing.
- Be ready to provide emergency CPR.

What happens at the hospital?
To make an accurate diagnosis, the patient will immediately have a CT or MRI scan and blood tests.
Treatment options may vary depending on the type of stroke.
A hemorrhagic stroke is when a vessel in the brain ruptures and a hematoma is formed, leading to swelling and compression of the brain. With large hematomas, sometimes only surgery can save a person. For small hematomas, doctors usually use diuretics to reduce the volume of fluid and carry out hemostatic therapy to stop bleeding from a ruptured vessel. The patient is constantly monitored to eliminate the risk of repeated bleeding.
The treatment is somewhat different in the ischemic type. It’s usually caused by a blood clot that plugs a blood vessel in the brain, disrupting blood flow. Spasmolytics, antihypertensive drugs, diuretics as well as drugs that improve oxygen flow are usually the choice in this case. The patient may also get thrombolytic medicine (a “clot-busting” drug) to break up blood clots formed in the affected vessel. In some cases, surgery – the removal of a blood clot – is the only option.