Risk factors:
The main risk factors for atherosclerosis can be classified into 2 categories:
non-modifiable factors and modifiable.
Non-modifiable factors:
Age
In the absence of other risk factors, atherosclerosis remains a natural occurrence with progressive deterioration of the qualities of the arteries according to age progression (women over 65 and men over 55).
Gender
Men are more likely to develop atherosclerosis.
Heredity
Patients with a family history of the disease are more likely to develop it.
Modifiable factors:
The main risk factor is smoking, closely followed by a sedentary lifestyle. Excess weight and obesity are also deciding factors, with the addition of Type 2 Diabetes.
It is also sometimes linked to menopause and oral contraception, but they are rarely the sole reasons for atherosclerosis.

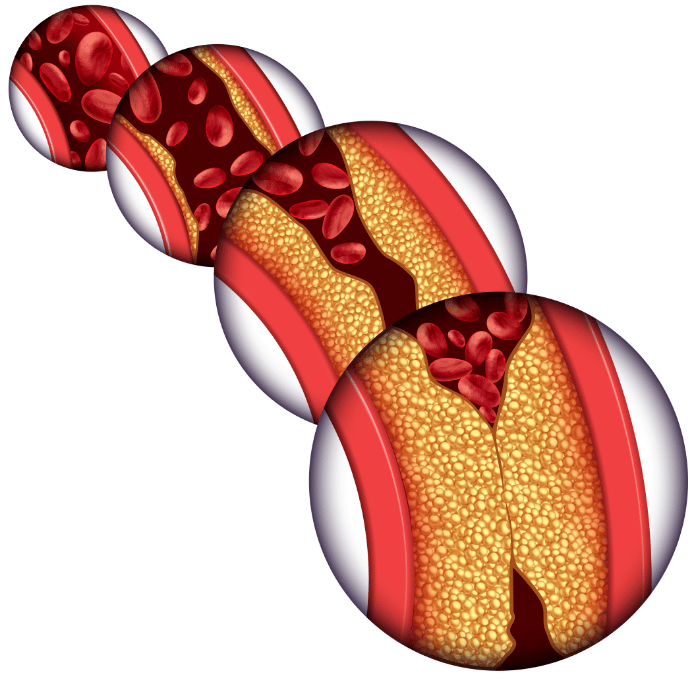
What are the complications of atherosclerosis?
When untreated, atherosclerosis can lead to many dangerous complications which may occur anywhere in the body.
The thickening of the vessel wall can block the artery, creating thrombosis, or stenosis, when the diameter of the artery decreases. The plaques can detach and cause embolism.
Vital organs, such as the heart and brain, might no longer function properly, which can lead to serious complications like myocardial infarction (or heart attack), a stroke, or an arterial aneurysm.